Round Robin
serverIndex = hash(key) % n: you have n cache servers, want to balance the load, then use: serverIndex = hash(key) % n
It is simple but when there is a server offline, n changed, it need rehashing and all server are routed to different cache, this may cause cache missmatch and traffic unbalance.
consistent hashing solve this problems effectively.
Consistent Hashing
use a hash ring to reduce the reshaing times. For example, SHA-1 use hash function f, the output range is [0, 2 ^ 160 -1]. each has will fall in one of the cells, connect tail and head, it forms a ring.
Hash servers: map the server based on server IP or name onto the ring. (say s0, s1, s2, s3)
Server lookup: to determine which server a key is stored on, we go clockwise from the key position on the ring until we find a server (s0, s1, s2, s3)
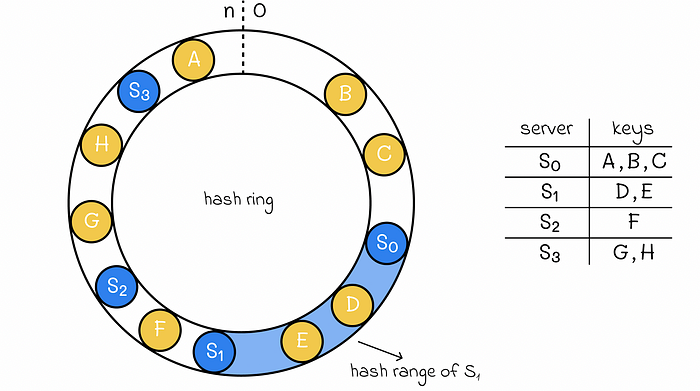
Add server: add a new server, it will redistribute the keys. say new server locate between s1 ans s2, then the key mapped to s2 need to redistributed, some of them will be mapped to new server.
Remove server: when server is removed, all keys in this server will go clockwise on the ring to the next server.
two issues
-
uneven size of partition: hash function can not keep the same size of partition on the rings. the server and keys distributed unevenly. -
uneven load: keys sometime located only on some server. the server load is unevenly.
Virtual Node
To solve above problems, we introduce virtual nodes, each server can be represented by multiple virtual nodes on the ring. In real-world systems, the number of virtual nodes is much larger
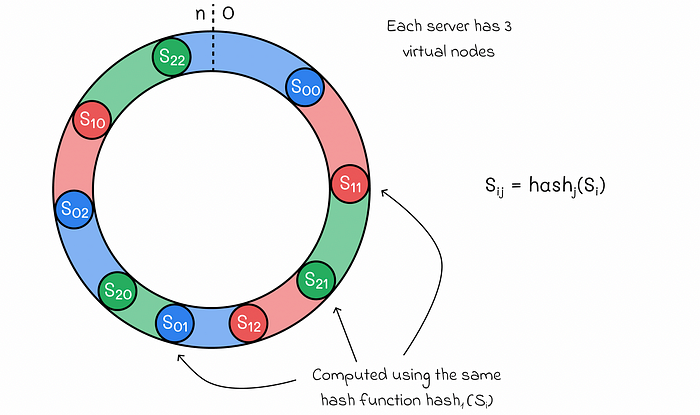
As the number of virtual nodes increases, the distribution of keys becomes more balanced.
This is because the standard deviation gets smaller with more virtual nodes, leading to
balanced data distribution. The standard deviation is between 5% (200 virtual nodes) and 10%
(100 virtual nodes) of the mean
ServerSwith higher capacity can have more virtual nodes than others
