Input: nums = [3,1,6,8], queries = [1,5]
Output: [14,10]
Explanation: For the first query we can do the following operations:
- Decrease nums[0] 2 times, so that nums = [1,1,6,8].
- Decrease nums[2] 5 times, so that nums = [1,1,1,8].
- Decrease nums[3] 7 times, so that nums = [1,1,1,1].
So the total number of operations for the first query is 2 + 5 + 7 = 14.
For the second query we can do the following operations:
- Increase nums[0] 2 times, so that nums = [5,1,6,8].
- Increase nums[1] 4 times, so that nums = [5,5,6,8].
- Decrease nums[2] 1 time, so that nums = [5,5,5,8].
- Decrease nums[3] 3 times, so that nums = [5,5,5,5].
So the total number of operations for the second query is 2 + 4 + 1 + 3 = 10.
Solution:
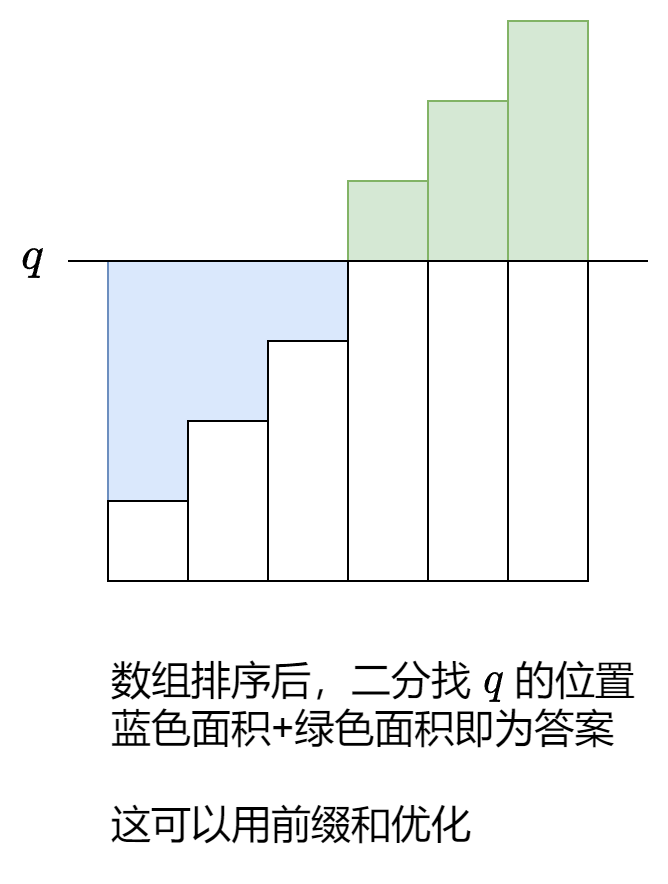
1)先sort,把队列变成升序,
2)然后二分法找到target,使得target左边是需要加,右边需要减。
3)用prefix sum得出左边的加总和右边的加总
class Solution {
public List<Long> minOperations(int[] nums, int[] queries) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n = nums.length;
long[] sum = new long[n + 1]; // 前缀和
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + nums[i];
}
List<Long> ans = new ArrayList<>(queries.length);
for (int q : queries) {
int j = lowerBound(nums, q);
long left = (long) q * j - sum[j]; // 蓝色面积
long right = sum[n] - sum[j] - (long) q * (n - j); // 绿色面积
ans.add(left + right);
}
return ans;
}
// 见 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1AP41137w7/
private int lowerBound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = -1;
int right = nums.length; // 开区间 (left, right)
while (left + 1 < right) { // 区间不为空
// 循环不变量:
// nums[left] < target
// nums[right] >= target
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid; // 范围缩小到 (mid, right)
} else {
right = mid; // 范围缩小到 (left, mid)
}
}
return right;
}
}
Input: nums = [1,3,1,1,2]
Output: [5,0,3,4,0]
Explanation:
When i = 0, nums[0] == nums[2] and nums[0] == nums[3]. Therefore, arr[0] = |0 - 2| + |0 - 3| = 5.
When i = 1, arr[1] = 0 because there is no other index with value 3.
When i = 2, nums[2] == nums[0] and nums[2] == nums[3]. Therefore, arr[2] = |2 - 0| + |2 - 3| = 3.
When i = 3, nums[3] == nums[0] and nums[3] == nums[2]. Therefore, arr[3] = |3 - 0| + |3 - 2| = 4.
When i = 4, arr[4] = 0 because there is no other index with value 2.
Solution: 实际上找的是相等元素之间的距离和
1)找出每个相等元素的index的list
2)对于每个list中的元素index,距离实际上就是把其他元素的index变成当前元素的index需要的操作数,这样套上个题目的模板即可
class Solution {
public long[] distance(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
var groups = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) // 相同元素分到同一组,记录下标
groups.computeIfAbsent(nums[i], k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(i);
var ans = new long[n];
var s = new long[n + 1];
for (var a : groups.values()) {
int m = a.size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
s[i + 1] = s[i] + a.get(i); // 前缀和
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int target = a.get(i);
long left = (long) target * i - s[i]; // 蓝色面积
long right = s[m] - s[i] - (long) target * (m - i); // 绿色面积
ans[target] = left + right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}

