Other References
digest
When talk about notification system, below features should be in your mind:
-
Notification Types:
- SMS
- push notification (app not in use like lock sreen message)
- in-app notification (app in use)
-
User preference:
- userId
- channel # push notification, email or SMS
- frequency (daily, weekly, monthly …)
- time (daytime on, night off)
- opt-in # boolean unsubscribe?
-
Template Management: Support for dynamic templates that can be personalized based on user data.
-
Retry-mechanism:
- fail message error handling, retry sending
- DLQ (manual intervention)
-
Scheduling & message priority:
- delayed or time-based notifications
- priority message (system alert) should be processed ahead of others
-
monitoring and Analytics:
- Queue status monitoring # auto scale worker nodes
- event tracking:
- sent error
- click
- unsubscribe
- delivered
-
Multi-Tenancy:
- support differenct client (with same system but isolate data)
non-functional requirements
-
availability: 99.99% uptime
-
latency: Low latency / eventual consistency
-
Fault tolearance
-
Data security: encrypt sensitive data, ensure GDPR
Traffic
QPS
Suppose system will handle 200 million notifications every day.
During peak hours like marketing campaigns or system-wide alerts, assume there will be 10 million messages per min. The peak traffic will last 10 mins.
The peak QPS is 10 million / 60s = 166k/s
Message Queue
knowledge in system design interview:
if message size is around 10k, generally one partition can handle 5k to 10k message per sec.
if message size is around 1k, generally one partition can handle 50k to 100k message per sec.
Assume each message size is 1k, then say one partition can handle 50k messages/sec, we need 4 * 50k > 166k, 4 partition to handle the traffic.
Storage
Assume each message size is 1k, then 200 million message per day need 1k * 200 million = 200GB/day.
That is 200 GB 365 5 = 365 TB for 5 years.
Bandwidth
for notifications, assume 50% are email, 30% are SMS, 20% are push notification. (need to consider the peak hour)
-
For Email: assume each email size 10k:
- 166k 50% 10k = 880M/s
-
For SMS: assume each text size 1k:
- 166k 30% 1k = 50M/s
-
For push: assume each notification size 500 bytes:
- 166k 20% 500 = 16.67M/s
total is 880 + 50 + 16.67 = 947 M/s
947 / 125 = 7.2 Gbps
high level architecture
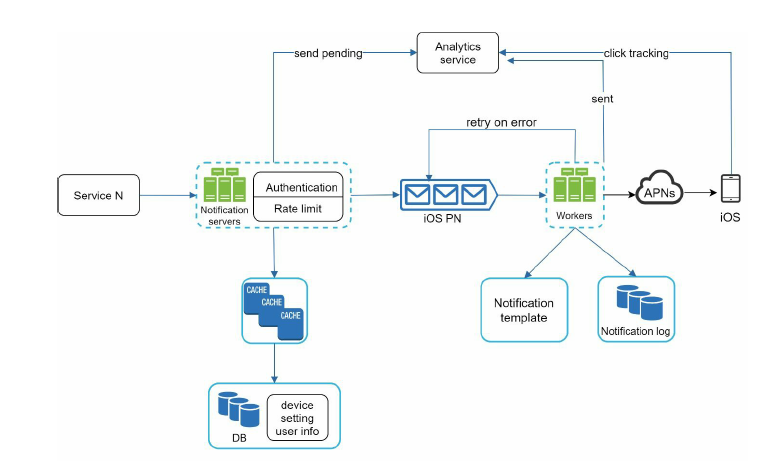
The worlflow of first version can be described from left to right.
Service N
Represent business services like billing service, payment service etc. these service call notification service to send notification.
notification service
In the first version of design, notification service handle api request and process notifications. This will cause the SPOF and has scalability issue and performance issue.
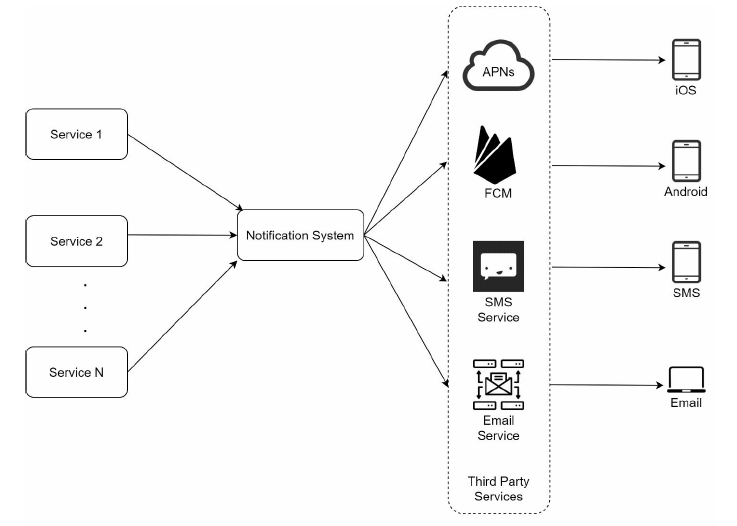
third party services
Third party services are responsible for delivering notifications to users. Note that integrated with third party should be flexible, as some of the service will be unavailable in the future. like FCM is disabled in China.
Improved design
-
Move the database and cache out of the notification server.
-
Add more notification servers and set up automatic horizontal scaling.
-
Introduce message queues to decouple the system components.
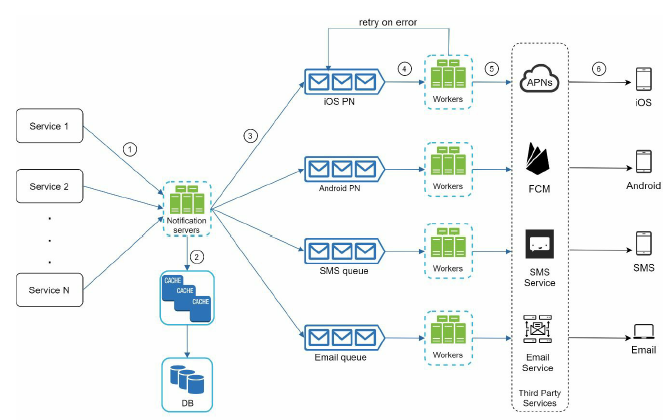
In this design, we add worker nodes to handle the message processing, this reduces the load of notification service. Notification service acts like a management service.
notification service
-
Provide APIs for services to send notifications. Those APIs are only accessible internally or by verified clients to prevent spams.
-
Carry out basic validations to verify emails, phone numbers, etc.
-
Query the database or cache to fetch data needed to render a notification.
-
Put notification data to message queues for parallel processing.
DB
store user preference, settings, we can extract a user preference service from notification service to handle this.
workers
woker nodes are responsible for consuming message from mq and send them to corrsponding third-party.
Deep dive
- additional feature:
- notification template
- user preference
- rate limiting
- retry mechanism
- security
- monitoring & event tracking
Reliability
To prevent data loss, we introduce retry mechanism. Sometimes due to the latency issue or retry, message will be consumed more than once. To prevent this, we assign an unique ID to each event, before processing, workers will check if the event is already consumed in DB.
monitoring & event tracking
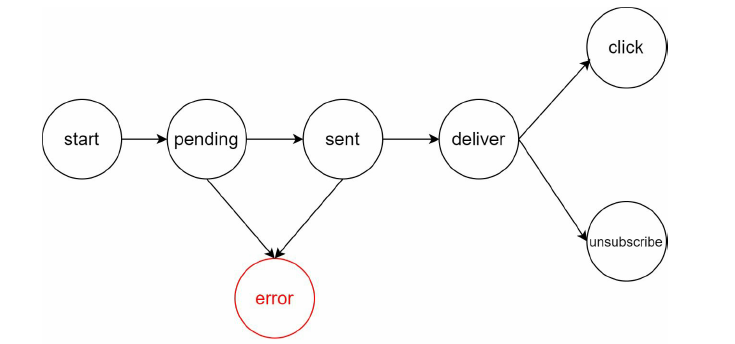
The final version would be: