Scale Route
1. Single server
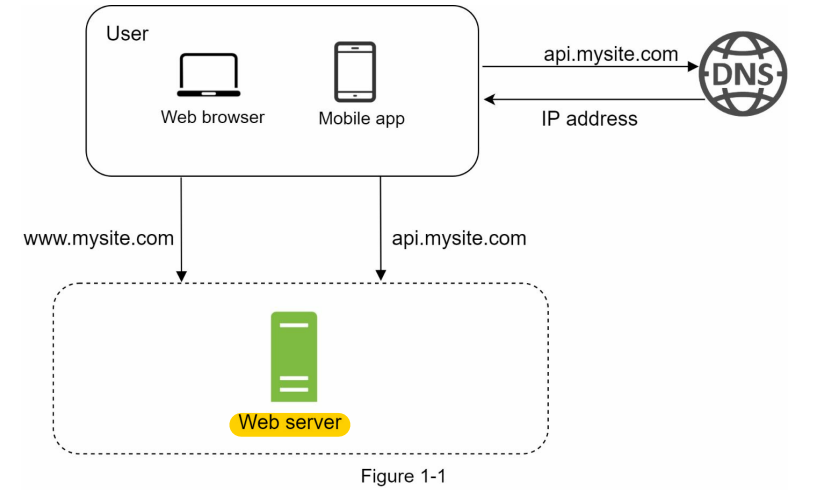
2. Database (separate Data tier and web traffic tier)
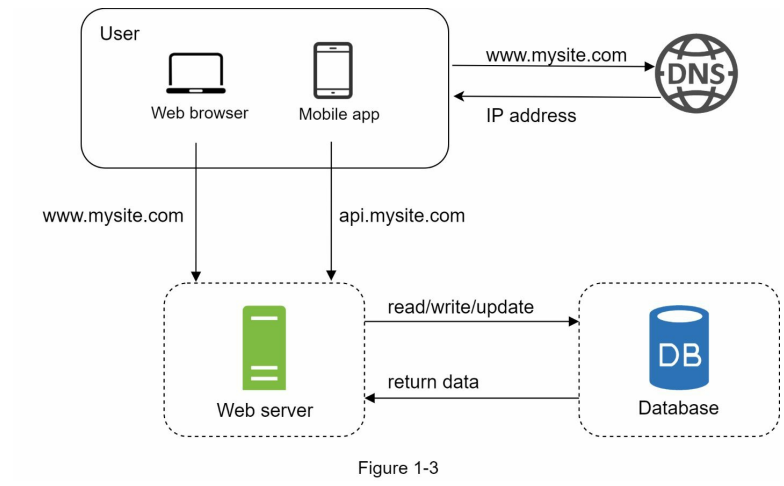
Choose which database to use, Nosql or relational database
Non-relational database might be the right choice if (easy to scale, no join operations):
- app requires super-low latency.
- data are unstructured or you do not have any relational data.
- only need to serialize and deserialize data (JSON, XML, YAML, etc.).
- store massive amount of data
3. Load Balancer
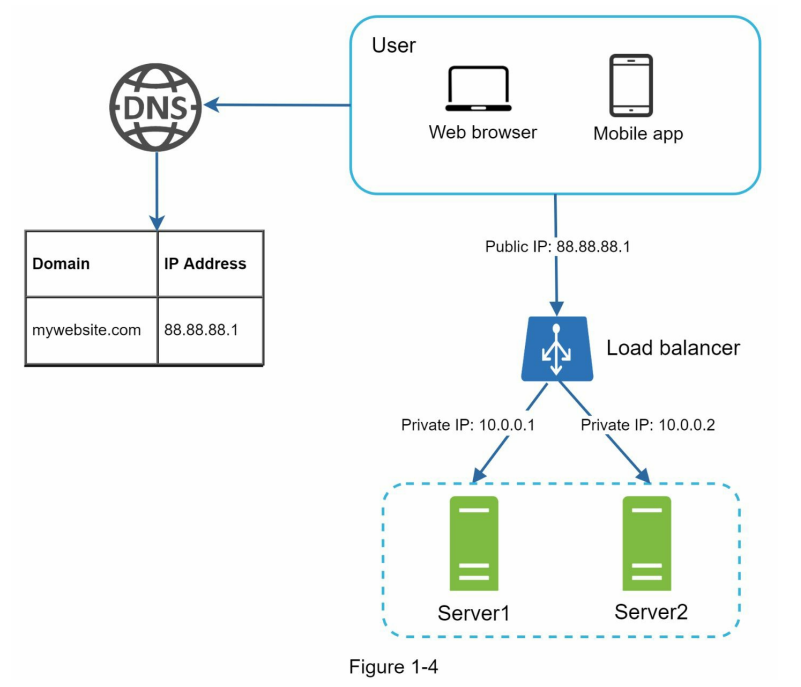
load balancer
- Balance the traffic, easy to scale server, just need to redirect the traffic to the latest added server
- Good security, as the entry point of the server using Public IP, hide the server behind with private IP
4. Database Replication
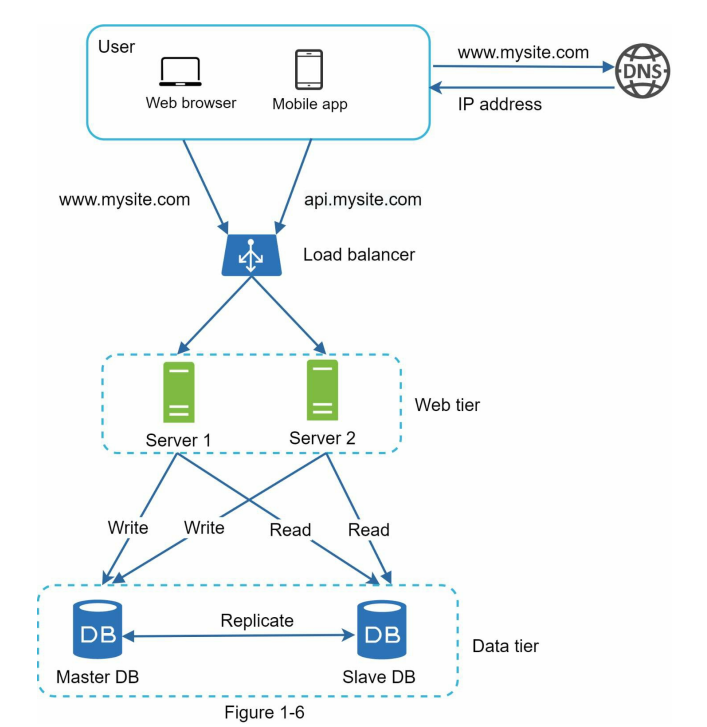
5. Cache
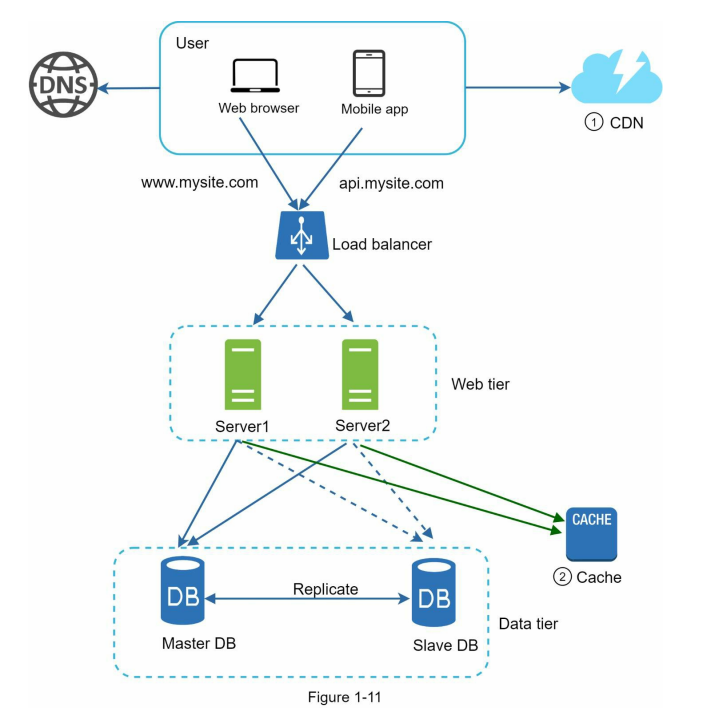
Add cache between DB and server, reduce response time Add CDN to cache static resources
6. Move session data to persistent database
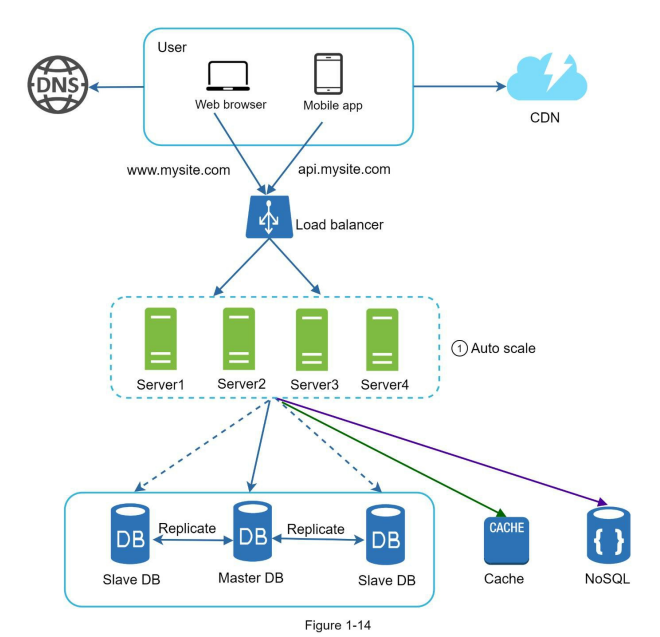
7. Data center
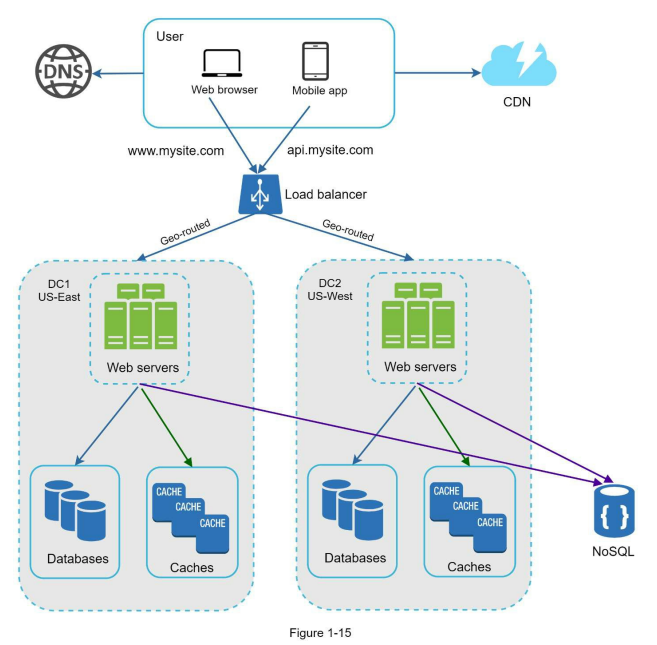
Lower latency for user in diff geo location
8. Message Queue, logging, metrics, automation
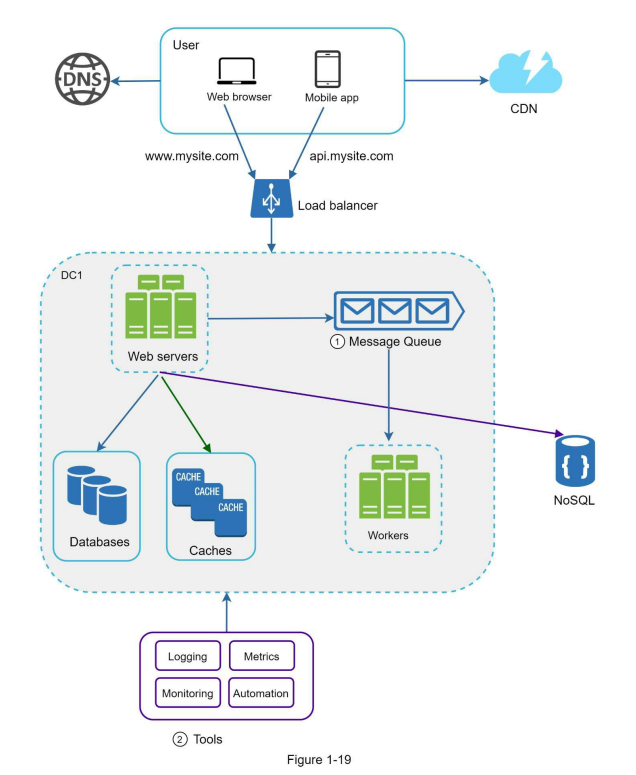
use message queue and worker nodes to async process jobs.
Basic Concepts
Database Replication - master slave

In this structure, master node only responsible for the write operation, Several slave nodes responsible for the read operations.
Benefit:
- Better performance: multi slave nodes support parallel read operation.
- Reliability: data is replicated across multiple locations, do not need to worry about data loss when one machine is down or destroyed
- High availability: master or slave down, DB can still be functional
When slave down, master take its job (if other slaves not available), new slave node take the job back, replace old node When master down, a slave promote to master, a new slave node will take old slave node job
DB scaling
Vertical scaling: add more powerful CPU, RAM to improve performance
- may have single point of failure
- expensive for scaling
- easily reach limit
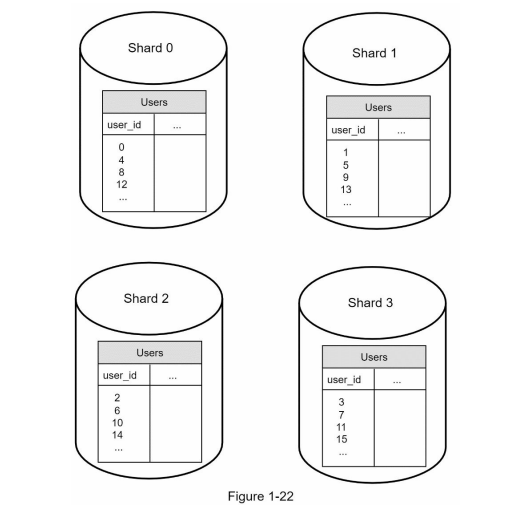
Horizaontal scaling: separate DB to serveral part called shard, it use a hash function to decide which shard goes into. For example, we separate the user schema into 4 shards based on user_id (called sharding key), the hash function we can use is hashcode = user_id % 4
- evenly distribute data
CDN
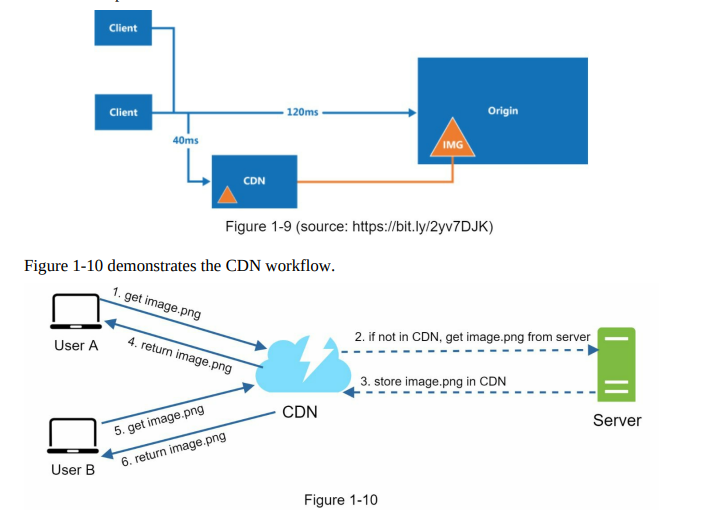
CDN is used to cache static resources like images, videos, CSS, JavaScripts etc (cache used to lower the response time)
- Cost: CDNs are run by third-party providers, only cache frequently used things in CDN.
- TTL: find an appropriate cache expire time
- CDN fallback: If there is a CDN outage, clients should be able to detect the problem and request from origin.
Invalidating files: You can remove a file from the CDN before it expires by performing one of the following operations:
- Invalidate the CDN object using APIs provided by CDN vendors.
- Use object versioning to serve a different version of the object. To version an object, you can add a parameter to the URL, such as a version number. For example, version number 2 is added to the query string: image.png?v=2
