OOD
management system OOD
Gym, Parking lot, Hotel, Library, Restaurant, etc.
When get the problem, think about if there is a management role in the system. If yes, it belongs to management system.
This kind of questions are frequently asked in interviews.
-
Clarify the requirements - What and How
Design a parking lot.
think about the nouns. –>
parking lot, and the noun related to the management -Vehicle -
Core objects - input and output
input : parking request
output: parking ticket/receipt -
Cases - use case
- Reserve
- Serve
- Checkout
-
Class - UML Diagram
receiptis important in magament system. It can be used to store the relationship between the management object and the user (book - user).create a class
receipt(many-to-many) instead of put one inside of the other (one-to-many).
Clarify
What : keyword is parking lot.
What does parking lot manage? –> Vehicle / ParkingSpot
for ParkingLot, what kind of parkingLot? –> multiple levels? (for some parking lots, one space may have upper space and lower space)
for Vehicle, what kind of vehicle? –> Car / Truck / Motorcycle
for ParkingSpot, what kind of parkingSpot? –> one spot for one car? or two spots for a bus?
Example:
Design a parking lot with multi-levels, vehicle has three types: car, truck, motorcycle.
How : think about the rules
-
How to park? to park a vehicle, we need to find a parking spot first. So parking lot should shows the available spots in each level.
-
How to charge? Free or charge by hour?
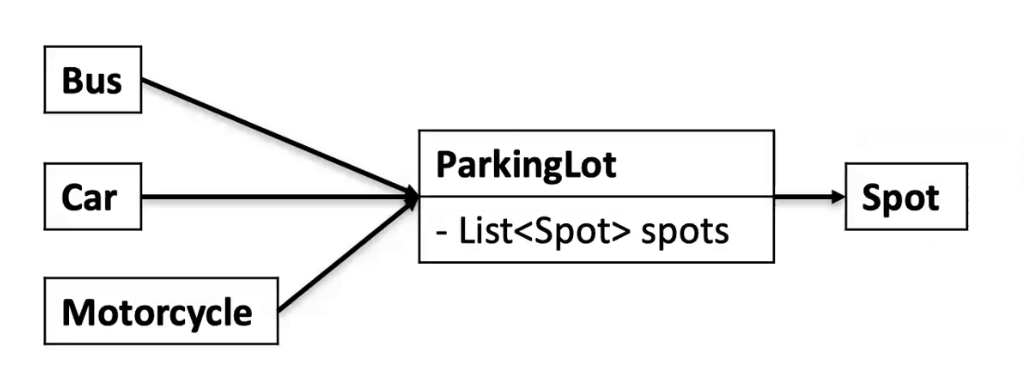
Core objects
Bus, car, motorcycle –> parking lot –> parking spot
prevent unnecessary objects.
bad example: parkinglot class contains a list of cars, we don’t need to store the cars in parkinglot class. Also this is tightly coupled.
Instead, we use a receipt class to store the relationship between the parkinglot and the car.
The final design is like this:
Cases
Two ways to think about the cases: Think as a user, or think as a manager.
-
As a user, I want to park my car, I need to find a parking spot first, then park my car. When I leave, I need to pay the fee, get the receipt.
-
As the problem itself, when a car comes, I need to find a parking spot for it. When the car leaves, charge the car, update the parking spot status.
During the interview, the second way is better.
For cars, we don't need it to provide any fuctions.
For parkingLot:
- Get available spots
- Park a vehicle
- Clear a spot
- calculate fee
Management common cases:
-
Reservation: X (ask interviewer)
-
Serve: Park vehicle, get available spots
-
Checkout: Clear spot, calculate fee
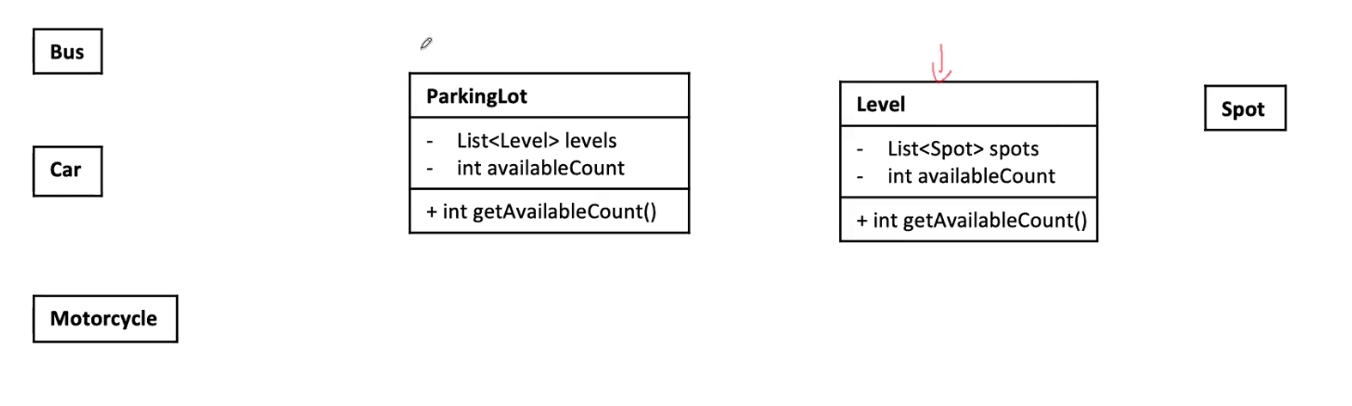
Class
1. Get available spots
parkingLot:
- List<Spot> spots;
- int availableSpots; add an attribute to store the available spots
---------------
+ int getAvailableSpots(); add a get method to get the available spots
Since it is multi-level parking lot, we create a class `Level` to store the spots in each level. And parkingLot contains a list of levels.
- Park a vehicle
-
check the size of the vehicle
- car object –> size, getSize()
-
find a spot for the vehicle
- parkingLot –> findSpot()
- level –> findSpot()
- spot –> isAvailable()
-
park the vehicle
- parkingLot –> park(vehicle)
- spot –> park(vehicle)
- spot –> free()
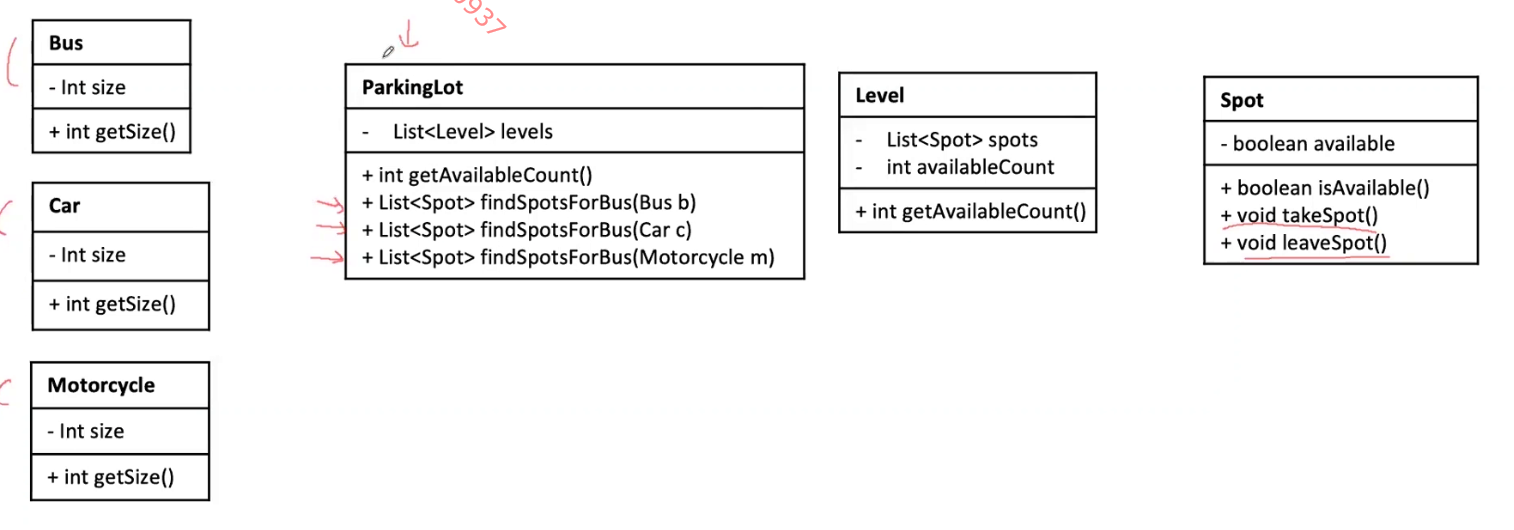
For Vehicle, three types of vehicle should extend the interface Vehicle.
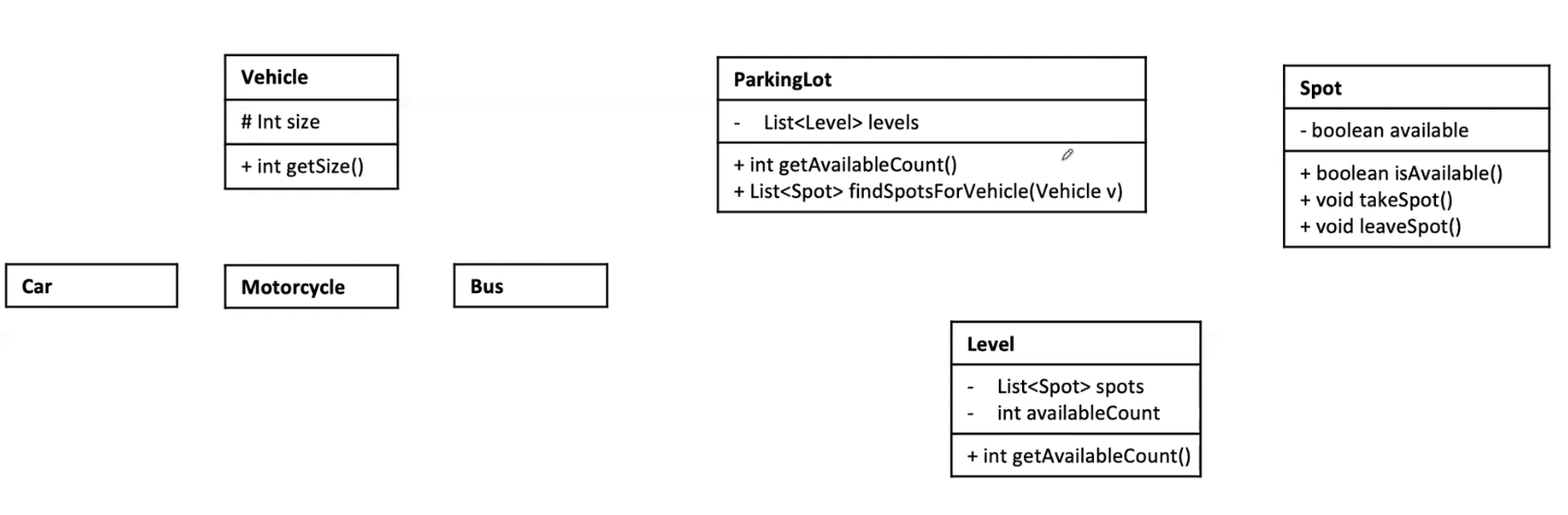
- Clear a spot
-
Parking lot find the spot to clear
-
update the spot status to available
if do not use receipt, we need to put spot in the vehicle class. Here we use receipt to store the relationship between spot and vehicle, update the UMl diagram:
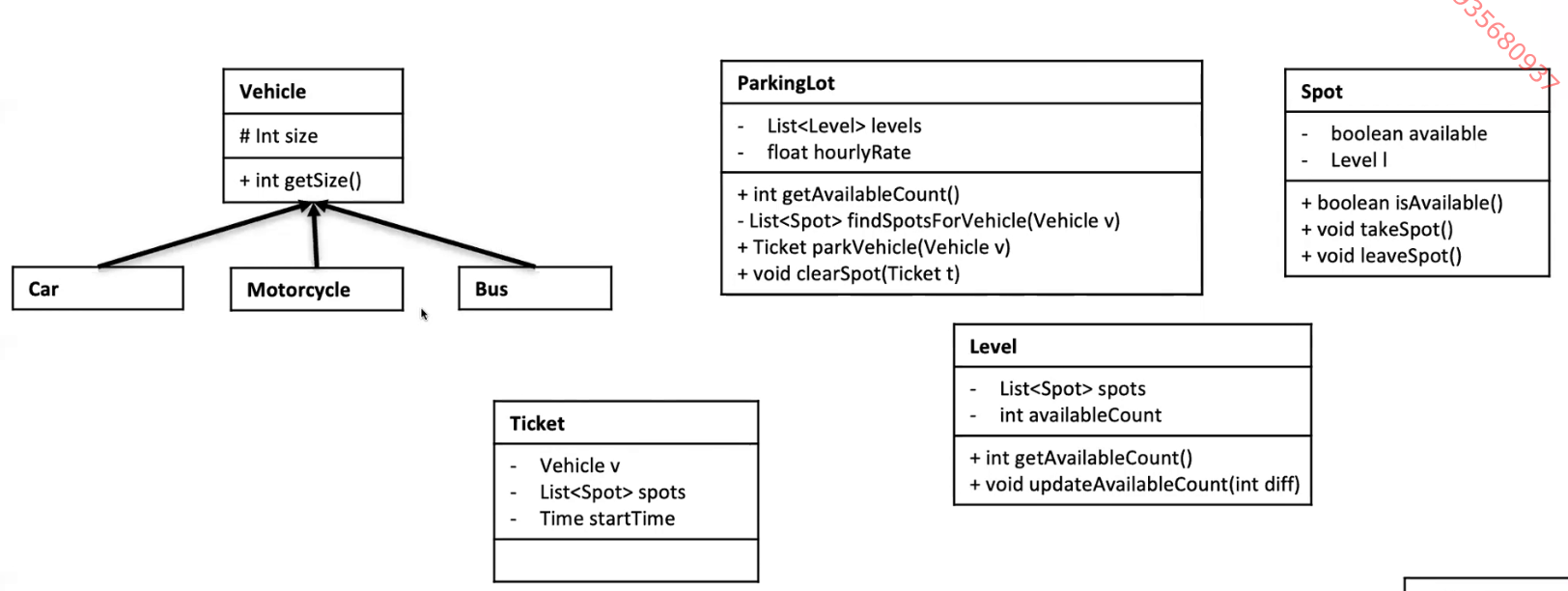
- Calculate fee
- parkingLot –> calculateFee(receipt)
calculateFee based on the start time and current time, times the rate.
Correctness
- Validate the use cases
- Follow good practices
- SOLID principles
- Design patterns
To add more features, we can set the parking lot as a singleton class
Reservations system
common problems: Hotel, Restaurant.
let’s start from a simple one: Restaurant (without reservation).
Clarify
What:Restaurant
What size of the tables, how many people can sit in one table?
How:
Does it have reservation system? –> No
Core objects
Think in this way: (this is actually the use case)
1. When party comes, find a table for them.
2. party have the menu, order meals, return the meals they ordered.
3. check out, clear the table.
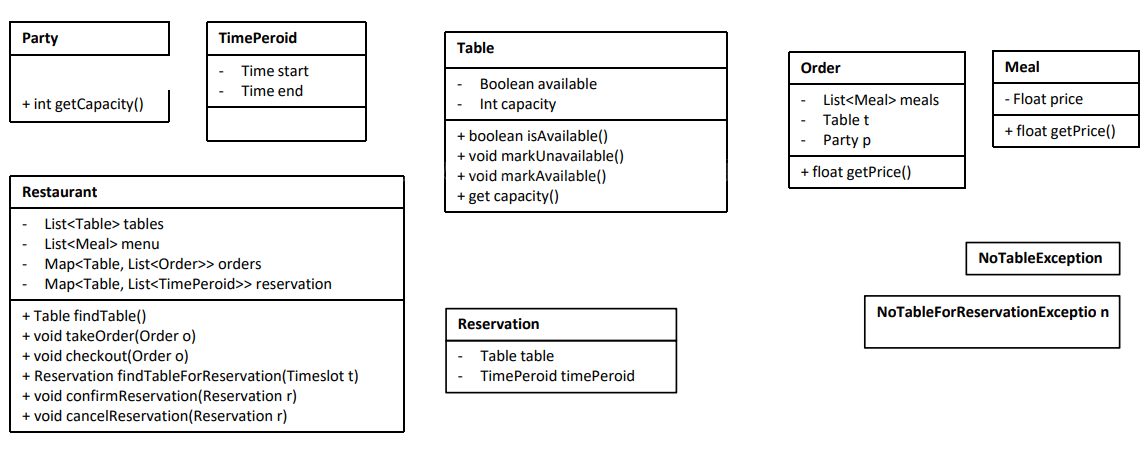
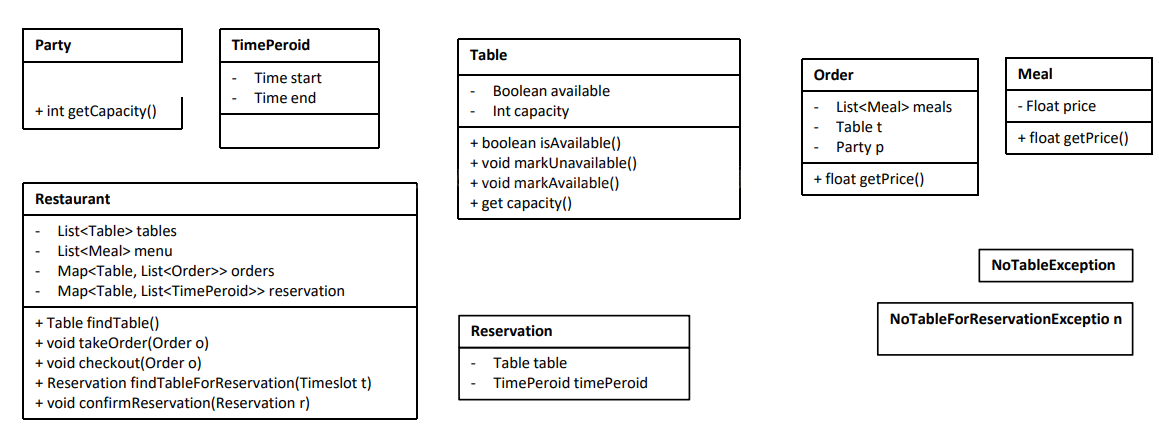
Restaurant, party, table,meal, order.
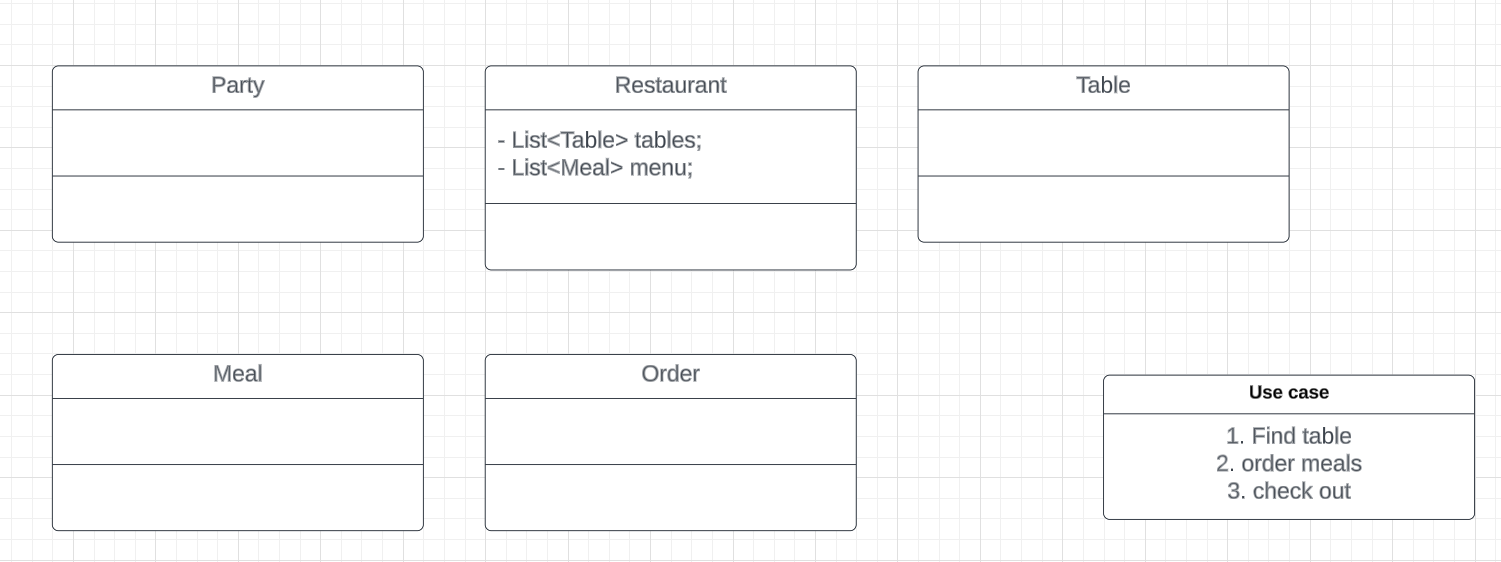
Cases
This step always comes with the core objects.
1. When a party comes, restaurant needs to find a table for them. --> find table
2. Party orders meals. --> order meals
3. finish the meal, check out. --> check out
Class
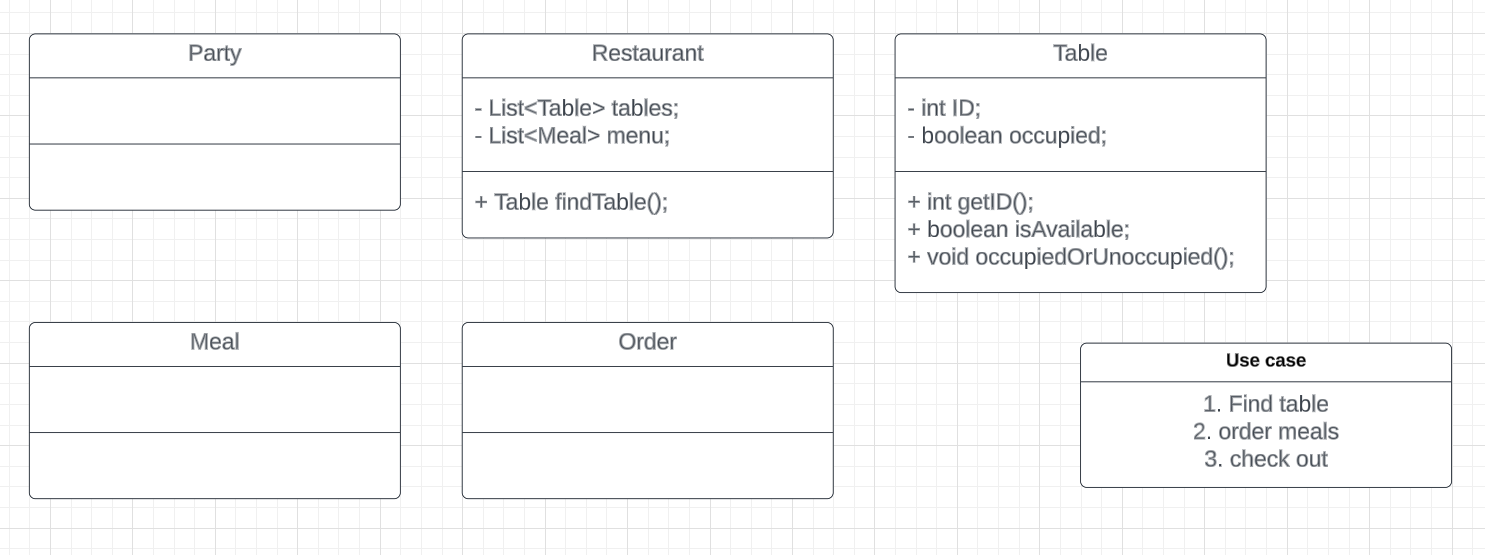
- find table
find a table, mark the table as occupied, return the table.
For Restaurant:
- Add a method `findTable()` in restaurant class, return a Table object.
For Table:
- Add a boolean attribute `available` in table class and a method `isAvailable()`.
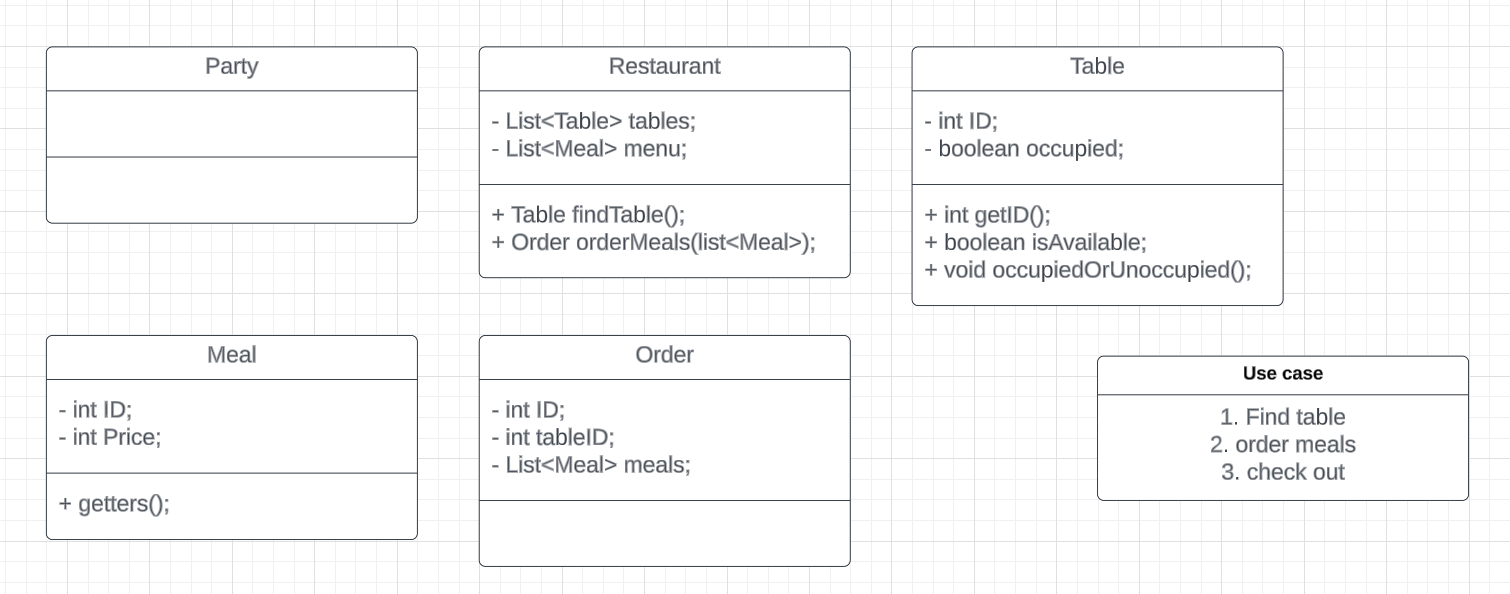
- order meals
order take a list of meals and return a order receipt.
For Restaurant:
- Add a method `orderMeal()` in restaurant class, return an Order object.
For Order:
- add a field `List<Meal> meals`
- add a field `int id`
- add a field `int tableId`
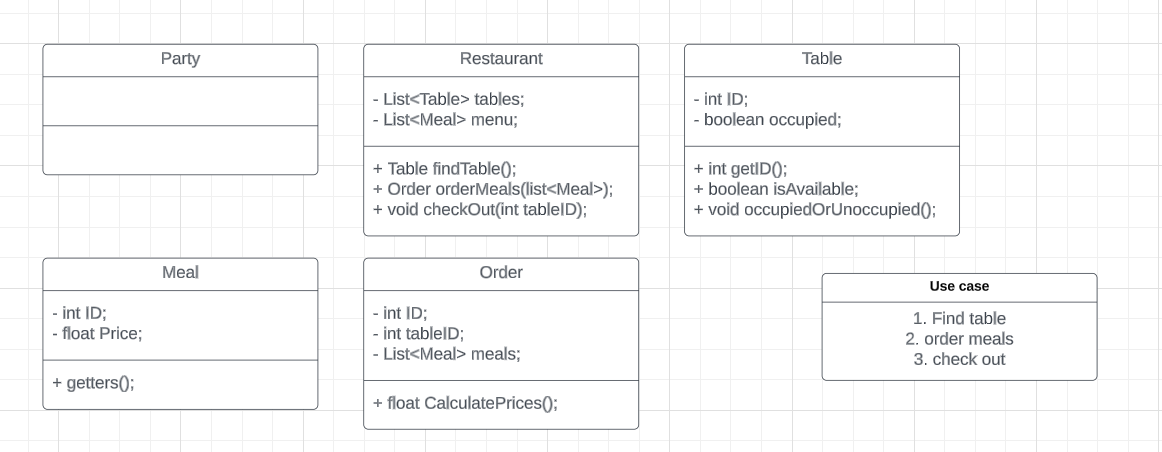
- check out
get the total price of the meals, clear the table.
For Restaurant:
- Add a method `checkOut(int tableID)` in restaurant class, no return.
For Table:
- Add a method `clearTable()` in table class, no return. (or use the occupiedOrUnoccupied method)
For Order:
- Add a method `calculatePrice()` in order class, return the price.
Correctness
review the use cases, follow good practices, SOLID principles, design patterns
Now let’s add the reservation system. For the reservation system, we can think in this way:
Search criteria -> Search() -> List<Result> -> Select() -> Receipt
search criteria: number of people, date, time, etc.
number of people: each table is the same size, the number of people would not exceed the table size.
date: What is the latest date we can reserve? --> 1 month
time: Does all time are available? --> Yes, we can reserve any time.
Search(): search the available tables based on the search criteria.
Add a method `findTableForReservation(Timeslot timeslot, int people)` in restaurant class,
1. return a List<Timeslot> (Reservation) object.
How long is the timeslot? --> 2 hours
2. Or we can go to the confirmation page directly. Or show not available message (throw exceptions).
Add Reservation class:
- add a field `int id`
- add a field `int tableId`
- add a field `Timeslot timeslot`
For Restaurant:
- Add a method `findTableForReservation(Timeslot timeslot, int people)` in restaurant class, return a Reservation object.
- Add a method `confirmReservation(Reservation reservation)` in restaurant class, return a Receipt object/ nothing.
Add NoTableAvailableException class
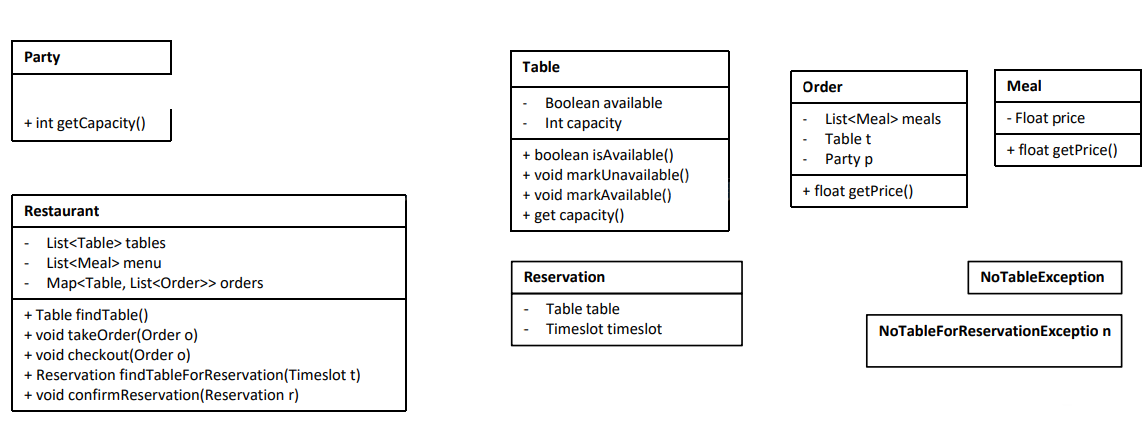
How do we know if the table is available?
For Table:
- add a field `List<Timeslot> reservedTimeslots`
To cancel the reservation, we can add a method in restaurant class:
add a method `cancelReservation(Reservation r)` in restaurant class, no return