What is ES6?
ECMAScript 6 is also known as ES6. It is used to create web applications. It is a programming language based on scripts that supports object-oriented and functional programming styles.
ECMA is the standard, JS is the language in practice
What are some new features introduced with ES6?
- Let, Const
- Arrow Functions
- Template string literals
- Map & Set
- Array & Object Destructuring
- Spread & Rest Operator (…)
- Enhanced object literals
- Default function parameters
- Generators
- Classes
- Promises
- Async/Await
- Modules
What is Hoisting?
Hoisting is a mechanism.
Before execution, all function and variable declarations are moved to top and scanned. So you can use a function or variable before declaring it without error.
“Function declaration” only applies to the keyword function declaration since the function expression & arrow function are assigned to variables.
What are the differences between Var, Let, and Const?
-
let are only available inside the block where they’re defined.
-
var are available throughout the function in which they’re declared, if defined outside a function block, it is global value.
-
Const are used to define values that are not changed.
What is the difference between == and ===?
-
== only compare values.
-
=== will check datatype and compare two values.
What does this refer to in JavaScript?
For object : refer to the instance of the object.
For Keyword Function : ‘this’ changes based on where it is invoked
For Arrow Function : in the scope where this is defined
What are JavaScript Scopes?
Scope: the section of code that can access a variable or function
-
Block : code within non-function body like for loop, static code block
-
Function : code within function bracket {}
-
Global : all codes not block or function
- Window : a global object that represents the current browser tab
What is closure in JavaScript?
an inner function with references to outer function scope and its variables. a closure gives you access to an outer function’s scope from an inner function.
What is Callback Hell?
nested callback functions whose arguments are results of the outer callback. - Difficult to read, maintain, debug. Use promise chain to solve this problem
What is a Promise?
an object that represents the eventual completion/failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value
Three states: Pending, Fulfilled, Rejected
- The promise will always log pending as long as its results are not resolved yet
- Once resolved, the status changed to fulfilled
- If an error occurs, the status will change to reject.
.then() : access a promise result with two options : success or failure callback, it will return a promise with pending status.
.catch() : generally put at the end of the chain, to handle errors.
Promise chain
consecutively invoking .then() on a promise, compared to nested callback funcs, clean, readable, easy for debug and error handling.
What is Event Propagation?
Events pass through every DOM node until it reaches the final phase or is stopped by your code
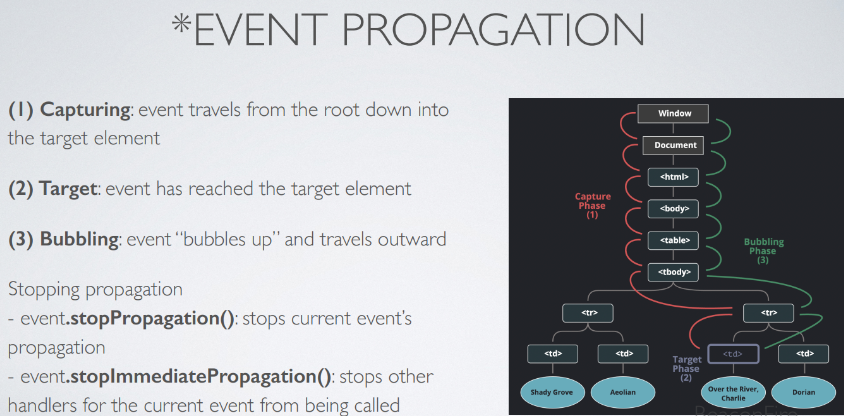
What is event.preventDefault?
prevent the default behavior of an element
Is JavaScript a single or multithreaded language?
JavaScript is a single-threaded language. It has one call stack and one memory heap.
JavaScript achieves asynchrony through the Event loop mechanism. It handles synchronous and asynchronous code.
What is the Event Loop? What do call stack and callback queue do?
Event loop : a runtime model that handles execution of synchronous and asynchronous code
Call stack : store the synchronous tasks
Task Queue:
-
Macrotask(callback queue) Queue → (event listener, timeout) low priority tasks executed when microtask queue is empty
-
micro task queue → async functions are executed when call stack is empty, promises have a higher priority than other asynchronous tasks (promise)
How does JavaScript compile (JIT)?
Just-in-time compilation
During runtime, entire code is converted into machine code, then executed immediately
What does it mean when we say that JavaScript is a Dynamically Typed Language?
Types are not specified when declaring variables; they are assigned based on the value at runtime.
What are some benefits of using Typescript?
A superset of JS, can not be directly executed by browser, needs to be transpiled to js.
Advantage:
- When cooperate with other teammates, build complex applications.
- Readable, easy for maintain.
- Catch errors before runtime like Type check
Disadvantage:
- Increase development time. Complex than js
What is Static Type Checking?
Type checking is performed without running the program.
What is an Interface in Typescript?
interface({}) defines object types (a group of key-value pairs) to be reused.
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
}
type alias (type) defines a type to be reused.
type Person = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
What is the difference between type any and type unknown?
-
any: can be assigned to any type, no type checking
-
unknown: can be assigned to any type, but type checking is required before using it
Code used to check value type for safety:
- Typeof
- Instanceof
- In
- Array.isArray()
