Create a Spring Boot Project
Open IntelliJ IDEA, click Create New Project and select Spring Initializr. Then click Next.
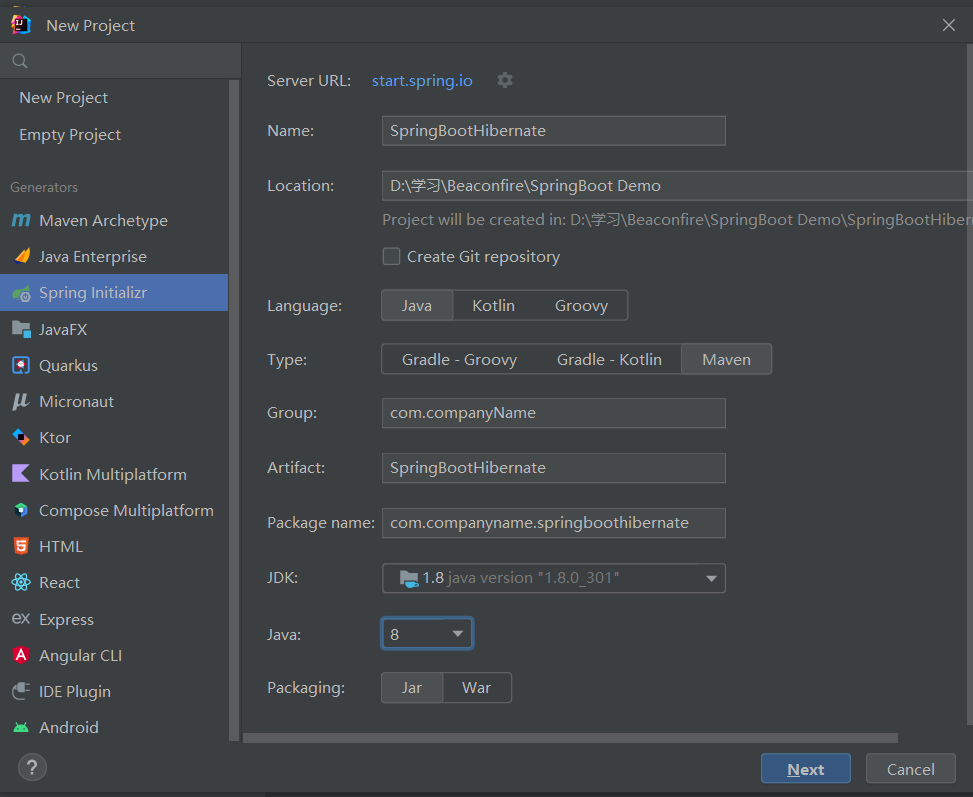
For the add on dependencies, we can add them later. Click Next and Finish.
Change the Java version to your current Java version.
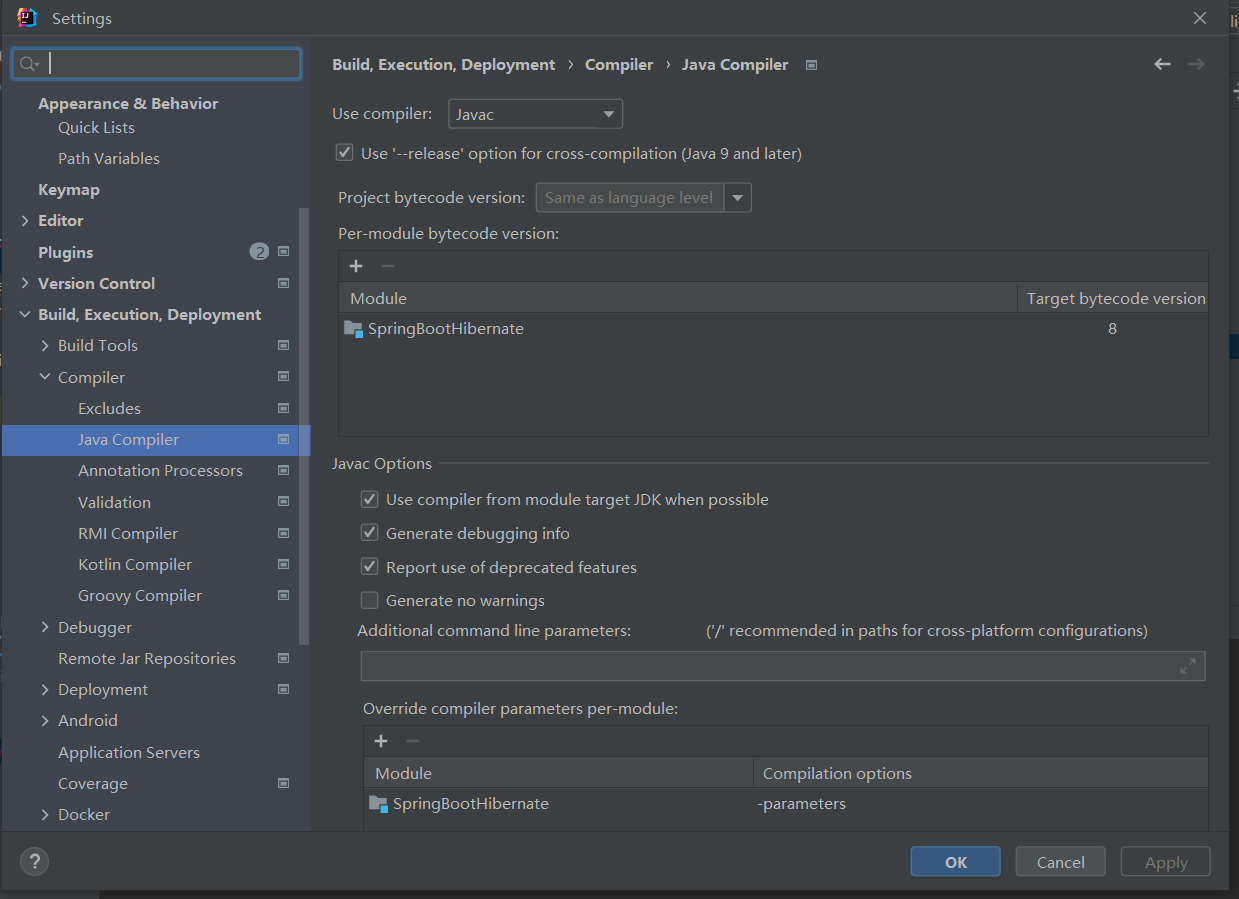
Also remember to change the Java version in pom.xml and the SpringBoot version:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<!-- version under 3 -->
<version>2.6.7 </version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
Connect to Database
JDBC
Add the following dependencies in pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.29</version>
</dependency>
Reload the project using Maven and we can see the dependencies. Java version
To connect to the database, we need to add the following configurations in application.properties:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/transactionDemo
spring.datasource.username=root
#NEVER store password as plain text in the property file or databases!!!
spring.datasource.password=password
Then create a configuration file for JDBC with DataSource.
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class JDBCTemplateConfig {
@Value("${spring.datasource.driver-class-name}")
private String JDBC_DRIVER;
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String DB_URL;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String USER;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String PASSWORD;
@Bean // register extra libs to spring container
public DataSource jdbcDataSource(){
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(getJDBC_DRIVER());
dataSource.setUrl(getDB_URL());
dataSource.setUsername(getUSER());
dataSource.setPassword(getPASSWORD());
return dataSource;
}
// getters and setters...
}
Then we can use JdbcTemplate to connect to the database, the common methods are listed below.
@Repository
public class QuestionDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private QuestionRowMapper questionRowMapper;
@Autowired
public QuestionDao(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate, QuestionRowMapper questionRowMapper) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
this.questionRowMapper = questionRowMapper;
}
// query for a list of Object using query() method
public List<Question> getAllQuestions() {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM question";
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, questionRowMapper);
}
// query for a single Object using queryForObject() method
public Question getQuestionById(Integer questionId) {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM question WHERE question_id = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, questionRowMapper, questionId);
}
// insert, update, delete using update() method
public void addQuestion(int categoryId, String description, boolean active) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO question (category_id, description, is_active) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, categoryId, description, active);
}
public void changeQuestionStatus(Integer questionId, boolean status) {
String sql = "UPDATE question SET is_active = ? WHERE question_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, status, questionId);
}
}
To map the result set to an object, we need to create a RowMapper class.
@Component
public class QuestionRowMapper implements RowMapper<Question> {
@Override
public Question mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Question question = new Question();
question.setQuestionId(rs.getInt("question_id"));
question.setCategoryId(rs.getInt("category_id"));
question.setActive(rs.getBoolean("is_active"));
question.setDescription(rs.getString("description"));
return question;
}
}
Now, with the JdbcTemplate and RowMapper, we can manipulate the database.
Hibernate
Add the following dependencies in pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> <!-- JPA -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <!-- MySQL -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14.Final</version>
</dependency>
Create a RESTful Controller
Add the following dependencies in pom.xml:
<!-- Notice that the spring-boot-starter-Tomcat is embedded in web here -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- Spring Web -->
</dependency>
Add @RestController annotation to the controller class. Also, we need to create the DTO classes to handle the request and response.
```Java
@RestController
public class DashBoardController {
private CategoryService categoryService;
@Autowired
public DashBoardController(CategoryService categoryService) {
this.categoryService = categoryService;
}
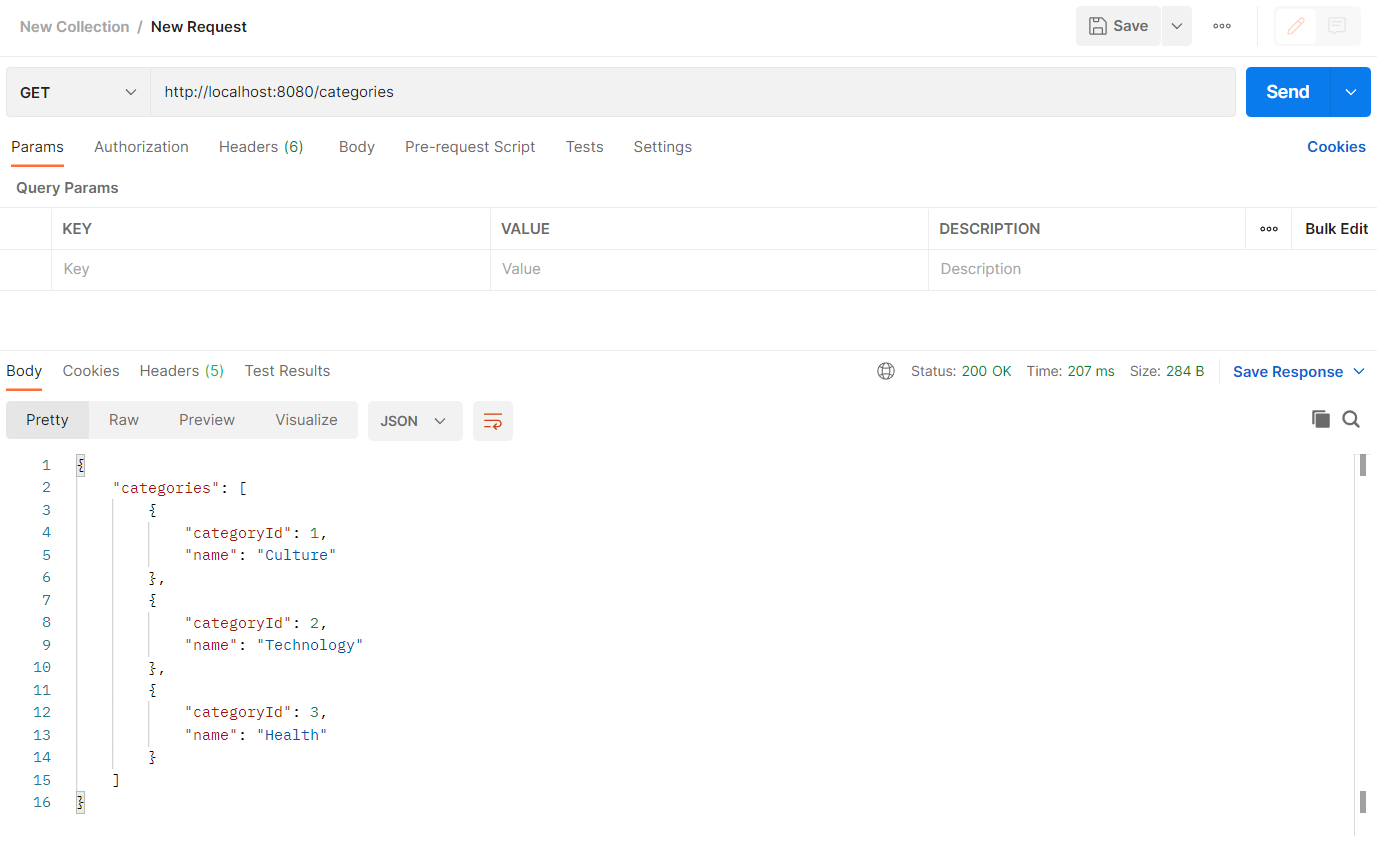
@GetMapping("/categories")
// @RequestBody ProductRequest productRequest
public ResponseEntity<CategoriesResponse> getCategories() {
// get all catogires
List<Category> allCategories = categoryService.getAllCategories();
return ResponseEntity.ok(CategoriesResponse.builder().categories(allCategories).build());
}
}
For the request and response, we need to create the DTO classes.
@Getter
@Setter
@Builder
public class CategoriesResponse {
// this is to map the response with the Json key
@JsonProperty(value = "categories")
private List<Category> categories;
}