JPA (Java Persistence API)
JPA is a specification of Java. It is used to persist data between Java object and relational database. It doesn’t provide any implementation, so it need a provider to implement it like Hibernate, EclipseLink, TopLink, etc.
-
ORM mapping between Java object and relational database
@Entityannotation is used to map Java object to relational database@Tableannotation is used to map Java object to relational database table@Columnannotation is used to map Java object to relational database column@Idannotation is used to map Java object to relational database primary key@Transientannotation is used to ignore the field when mapping Java object to relational database
-
JPQL (Java Persistence Query Language)
- JPQL is a query language which is used to query data from relational database
- JPQL is similar to SQL, but it is object-oriented
- JPQL is database independent
-
EntityManager
- EntityManager is used to manage the lifecycle of entity, and perform CRUD operations.
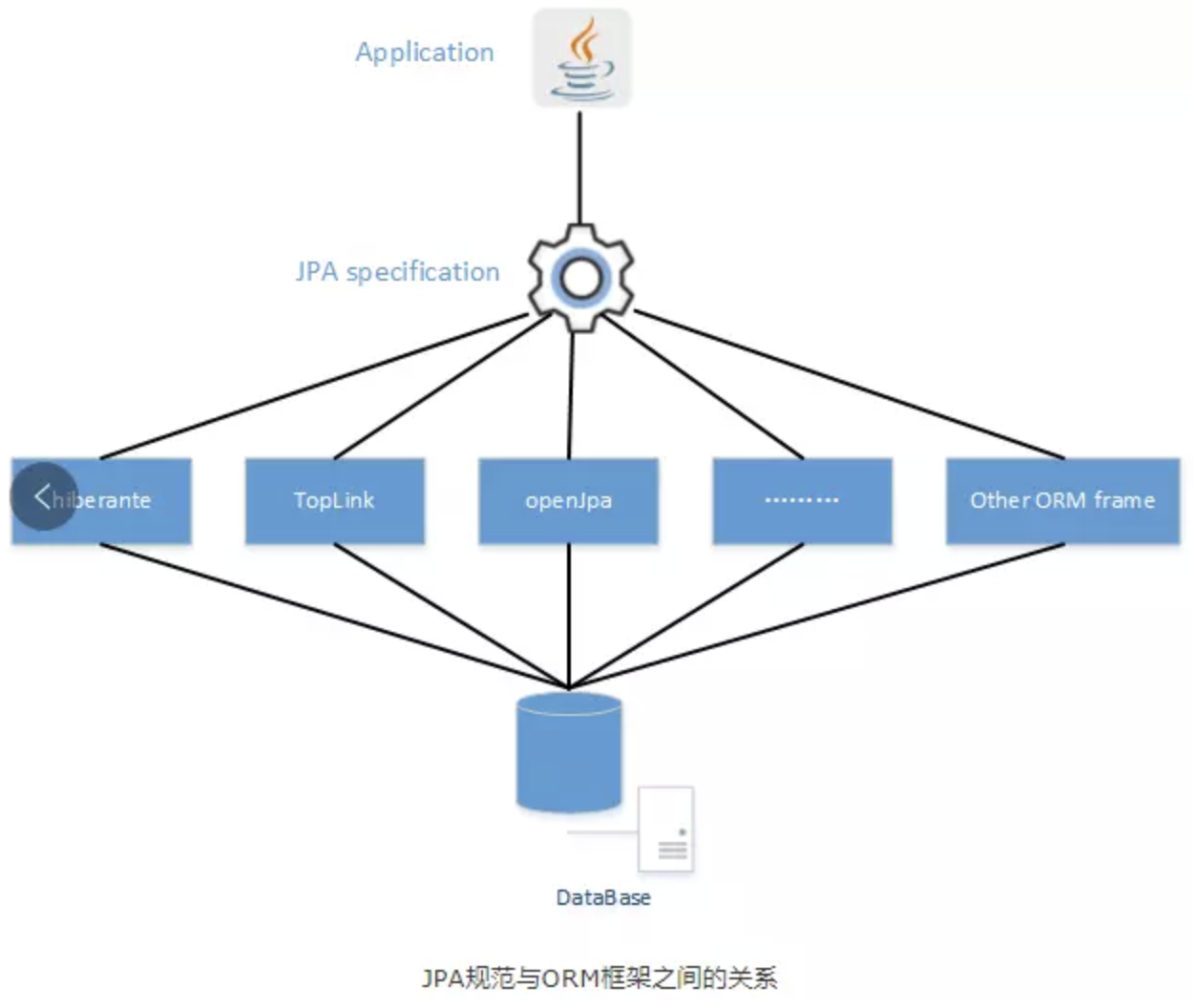
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA is a framework which is built on top of JPA. It is used to simplify the development of JPA application.
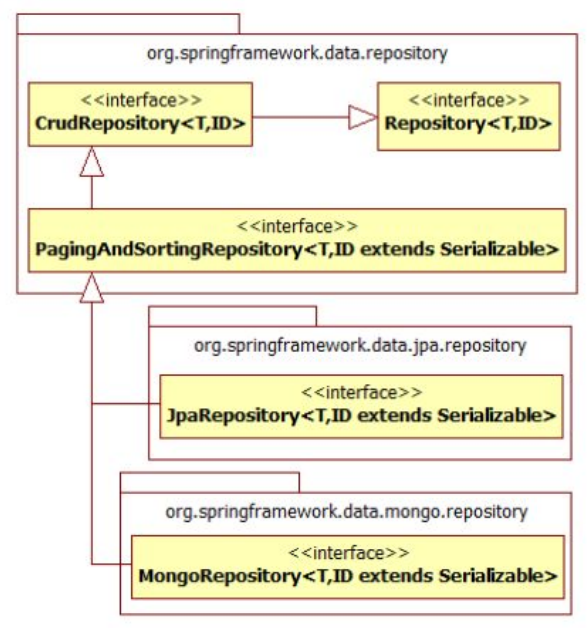
Spring Data Repository
Spring Data Repository has different interfaces, and each interface is used to perform different operations.
-
Repositoryis the central interface in Spring Data repository abstraction. It is amarker interfaceto capture the types to work with and to help you to discover interfaces that extend this one. It is not used directly. -
CrudRepositoryprovides CRUD operations, it extendsRepositoryinterface.public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> { // Note that the ID here is a serializable which represent the id of the Entity <S extends T> S save(S entity); Optional<T> findById(ID primaryKey); Iterable<T> findAll(); long count(); void delete(T entity); boolean existsById(ID primaryKey); // … more functionality omitted. } -
PagingAndSortingRepositoryprovidespaginationandsortingoperations, it extendsCrudRepositoryinterface.public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> { Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort); Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable); } -
Query Feature
Using Spring Data Repository, we can define the query method by using the naming convention. In this way, we don’t need to write the query statement and the implementation of the query method.
The machanism strips the prefixes
find…By,read…By,query…By,count…By, andget…Byfrom the method and starts parsing the rest of it.interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> { List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname); // Enables the distinct flag for the query List<Person> findDistinctPeopleByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname); List<Person> findPeopleDistinctByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname); // Enabling ignoring case for an individual property List<Person> findByLastnameIgnoreCase(String lastname); // Enabling ignoring case for all suitable properties List<Person> findByLastnameAndFirstnameAllIgnoreCase(String lastname, String firstname); // Enabling static ORDER BY for a query List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameAsc(String lastname); List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameDesc(String lastname); }We can also use
@Queryannotation to define the query method.interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> { @Query("select u from User u where u.emailAddress = ?1") User findByEmailAddress(String emailAddress); }
