java API
project story
Angular
React
JavaScript
Java Basic & Java 8
AWS Lambda & Step Functions
AWS Lambda is a computer service that allows us to run code without deploying and managing server. It is event-driven. Events, such as changes in an S3 bucket or an API Gateway request, trigger the execution of this function. It is used to run small tasks like get real time data flow, with 15 minutes maximum execution time.
AWS Step function is a serveless workflow service which allows us to coordinate multiple tasks such as lambda functions. With the help of step functions we can easily visualize our lambda function workflow and make adjustments based on our needs.
Limitation : limited memory and tempary storage. max execution time is 15 minutes. should optimize the usage of lambda or it will be expensive.
Spring Framework (IOC)
Core feature is Dependency Injection (IOC) - Invert the control of creating objects to the framework.
IOC Container types
BeanFactory: lazy loaded, XMLApplicationContext: eager loaded, XML & annotation
IOC Container life cycle
- IOC container
instantiatewhen spring application starts - Read the
beanclass from config files such as XML or annotations like @ComponentScan Createbean instance based on the Bean definition- inject the Bean when required
- Post-processor
callbackmethods, postProcessBeforeInitialization and postProcessAfterInitialization are called for monitor works or proxying.
Bean & Bean scopes
Bean is object managed by Spring IOC container. use @Scope to specify the scope of the bean.
Singleton:default scopeonly created once during Spring application run timePrototype: new instance per requestRequest: new instance per HTTP requestSession: new instance per HTTP sessionGlobalSession: new instance per global HTTP session
Dependency Injection (Ambiguous)
Constructor:@Autowiredon the constructor (inject immutable class)Setter:@Autowiredon the setter method (when circular dependency exist)Field:@Autowiredon the field (tight coupling, not recommended)
If there are multiple beans that implement the same interface, the container will not know which one to inject, We can use @Primary to determine which bean has higher priority, or use @Qualifier to specify an exact bean
Spring Boot (auto configuration)
Spring Boot’s core feature is Auto Configuration, which is used to reduce the time for setting up configurations.
-
Pomfile, spring Boot will generate default dependencies for us likesecurity,web,JDBC. -
application.propertiesfile, we canoverridethe default configuration by providing thekey-valuepairs in the application.properties file. like the data source url, username, password. -
@SpringBootApplication-
@EnableAutoConfiguration: Allows auto configuration based on the .jar dependencies in the pom.xml file -
@ComponentScan: scan the@Componentand their child class like @Controller, @Repository under the basic folder. -
@Configuration: Spring Boot will only scan @Bean third party class under the @Configuration class. This is used to add extra beans to the spring container.
-
Spring MVC
-
DispatcherServlet (central servlet)
map the requestto the corresponding controller method. -
Data is processed In controller, service, dao, and then return to the controller.
-
Controller create
model objectcontains the data in akey-valuepair way. Controller will return a string of the view name to theview resolver. -
View resolver has two responsibilities
-
prefixandsuffixto the view name to find the jsp page -
reach the template to replace the variables with the data in the model object.
-
Spring AOP
AOP is used to decouple cross-cutting concerns from the core business logic. (e.g. logging, exception handling) using proxy to wrap the object being called. intercept the calls and add extra functionality before or after the method call.
-
Join pointit is theunit of pointcan be monitored. -
Pointcutis a predicate or expression that matches join points. It is aset of join pointswhereadviceshould be executed. -
Adviceis theactionexecuted on join points. Different types -before,after,after-returning,after-throwing, andaround. -
Aspectis a module that encapsulates join points, pointcuts, and advice. It is a class that implements cross-cutting concerns.
Spring Security
Framework to protect our endpoints.
- Login in with username and password:
-
UserDetailsService
loadUserByUsername()to load user information from database, and then compare the credentials. -
AuthenticationManager
authenticate()to authenticate the user and generateUserDetailsobject with GrantedAuthority. -
Generate token with UserDetails.
- user want to access the endpoint with token: first it will be filtered by the filter chain.
-
JwtTokenUtil resolve() the token from request and generate the
userDetailsobject. -
generate authentication object and set the authentication object to SecurityContext.
For authroization, we can use @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") or @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('unverified')") to check the role of the user. Also, we can use @AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetails userDetails to get the user details in the controller.
JWT (JSON Web Token)
JWT is a standard that allows you to encode data in a JSON format. It is often used to encode authentication information, like the username, the permissions, etc. It is often used in combination with OAuth2.
JWT mainly contains three parts:
- Header:
Hashing algorithmused to sign the token. - Payload: contains the
claimslike userId, the permissions, etc. - Signature: is used to
verifythat thesenderof the JWT and to ensure that the message wasn’t changed along the way. (Created by hashing the header and the payload with a secret key)
Spring Scheduler (cron expression)
execute tasks for each period of time. @Scheduled annotation is used to specify the cron expression.
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000): execute the task every 1000ms.@EnableScheduling: enable the scheduling in the application.
What if two servers are running the same task? How to avoid duplicate execution?
Distributed Lock: use Redis to implement distributed lock. Acquire a distributed lock before executing the scheduled task.
Cache - (stale data)
Problem: When we update the data in the database, the cache is not updated. So the data in the cache is stale.
- Set expiration times for cached items.
- Use
@CacheEvictto remove the cache when updating the data. - Use
@CachePutto update the cache when updating the data.
Spring Profile (switch between different environments)
Spring profile is used to configure the application for different environments.
We can use @Profile to specify the profile for the class or method. We can use spring.profiles.active to specify the active profile in the application.properties file.
-
Add
@Profileannotation to the configuration class.@Configuration @Profile("dev") public class DevConfig { // ... @Value("${spring.datasource.url}") private String url; } -
Add
spring.profiles.activeinapplication.propertiesfile.spring.profiles.active=dev
Rest Controller & Input Validation (BindingResult) & RestTemplat
@RestController VS @Controller
@RestController is a convenience annotation that combines @Controller and @ResponseBody. It is used for building RESTful web services that return data in response to HTTP requests in JSON/XML. We don’t need to add @ResponseBody to our request mapping methods one by one.
@Controller is a common annotation that is used to mark a class as Spring MVC Controller while @ResponseBody is used to indicate that the return value of a method should be used as the response body of the request.
@RequestBody VS @ResponseBody
@RequestBody is used to map the content of an HTTP request body to a Java object, so you can access the data sent by the request in Java.
@ResponseBody is used to map the return value of a method to an HTTP response body, so you can return Java objects as data in the response.
How to validate the values of the request body? How does BindingResult work?
-
For the DTO classes, we can use
@NotNull,@NotEmpty,@Size, etc. to validate the values of the fields. -
In the controller method, we can use
@Validto validate the values of the request body.
BindingResult is used to validate the values of the request body. It is used to store the result of the validation and has to be placed right after the request body parameter. We can use hasErrors() to check if there is any error and handle the error in the way we want.
RestTemplate
RestTemplate is a tool provided by Spring to simplify the HTTP request to external Restful API.
The advantage is that it is easy to use, but the disadvantage is that the request URL is hardcoded, not good for decoupling. Also, it is synchronous, which means that the thread will be blocked until the request is finished.
RESTFul API 6 principles
-
Uniform Interface: requests looks same -
Client-Server decoupling: client and serverindependentof each other. Client -user interfaceand server -backend data storage. Communicate through REST API. -
Stateless:server X store client data. Each request contain all the information needed. -
Cacheability: When possible, resources should be cacheable on the client or server side. -
Layered System: Client does not need to know the internal structure (server / intermediary). -
Code on demand: The server can provide executable code or scripts for the client to execute in its context.
SOAP
SOAP is a protocol that uses XML to exchange information between computers over the Internet. It is an XML-based protocol for accessing web services. Compared to REST, SOAP is more difficult to implement and requires more bandwidth and resources.
Soap document need to have a root element called <Envelope>, which is required, and <Header> and <Body>, which are optional.
- Header: contains routing and processing information.
- Body: contains the actual message.
Microservices
API Gateway
API Gateway is a single entry point for all the microservices. Route requests to the appropriate microservice. It is not necessary, but it is good for decoupling and load balancing (round robin).
Application Monitoring (Actuator & Euraka)
-
Actuatoris used to monitor the application. It provides a lot of endpoints to monitor the application, such as/health,/metrics,/info, etc. (spring-boot-starter-actuator) -
Eurekais used to monitor the microservices. It is a service registry that is used to register the microservices. (spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server)
Microservices Debug (Logging & Distributed Tracing)
-
Centralized logging:
ELK(Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) to centralize the logs from different microservices. -
Distributed tracing:
Zipkin, use Zipkin to trace the request from the client to the microservices.
When Bug happens, we can use the traceId to trace the request from the client to the microservices. Then we can use the traceId to search the logs in the ELK to find the bug.
Kafka
Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that is designed for high-throughput, and real-time data processing.
Broker, Topic, Partition, Producer, Consumer, Consumer group, zookeeper
Fault-Tolerance
Enables system to continue works though there are some failures inside of it.
The more faults a system can tolerate without failing, the more fault-tolerant it is.
-
Circuit breakerscan prevent repeated requests to a failing service, allowing it time to recover. (Hystrix, Resilience4j) -
Timeouts can prevent a service from waiting too long for a response from another service. Fail fast is better than waiting indefinitely.
-
load balancers:avoid routing trafficto unhealthy instances.
JDBC & statement
JDBC is a Java API used to connect and execute query to the database. It uses JDBC statements to execute queries.
There are three types of JDBC statements:
-
Statement: Used to execute static SQL statements with no parameters. Actually we can pass parameters by concatenating strings, but this is not recommended because it is vulnerable to SQL injection attacks. Such asSELECT * FROM users WHERE username = 'admin' OR 1=1;will return all the users. So we should usePreparedStatementinstead. -
PreparedStatement: Used to execute static SQL statements with parameters. we can use?to represent the parameters, and then usesetXXX()method to set the parameters. It can prevent SQL injection attacks. -
CallableStatement: Used to execute stored procedures in database.
public static List<Trainee> getTraineesByPhoneNumber(String phone){
List<Trainee> trainees = new ArrayList<>();
// set up the connection
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
// Register JDBC driver, open a connection
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD);
// Execute a query
String query = "select * from trainee where phoneNumber = ? ";
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(query);
preparedStatement.setString(1, phone);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// retrieve data from result set row by row
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String firstName = resultSet.getString("firstName");
String lastName = resultSet.getString("lastName");
String phoneNumber = resultSet.getString("phoneNumber");
String ssn = resultSet.getString("ssn");
Trainee trainee = new Trainee(id, firstName, lastName, phoneNumber, ssn);
trainees.add(trainee);
}
resultSet.close();
// Clean-up environment, handle exceptions
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return trainees;
}
Transaction Management
Transaction is a set of operations that are executed as a single unit of work. If one operation fails, the whole transaction fails. In JDBC, the Connection interface provides methods to manage transactions. There are three methods in the Connection interface: setAutoCommit(), commit() and rollback().
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD);
statement = conn.createStatement();
// 1. setAutoCommit(false) to disable auto-commit mode
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String query = "update Bank set balance = 100 where accountName = 'April'";
statement.executeUpdate(query);
// ... several other executions
// 2. setAutoCommit false all the operations are grouped together and committed at once
conn.commit();
System.out.println("Transaction successfully committed");
System.out.println(getCurrentBalances(statement));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
try {
System.out.println("rolling back ...");
if (conn != null) {
// 3. rollback if any exception occurs
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JDBCTemplate
JDBCTemplate is a class in Spring JDBC, which is used to simplify the use of JDBC and avoid repetitive code.
All we need to do is pass the SQL statment, RowMapper and parameters to the JDBCTemplate object, and then it will fetch the data from database and convert it to the object according to the rowmapper.
main methods:
queryForObject: return a single objectquery: return a list of objectsupdate: update the database
Hibernate
Hibernate is an ORM (Object Relational Mapping) framework, which is used to map the object-oriented domain model to the relational database.
ORM
To configure Hibernate:
-
Add the dependency in pom.xml
-
Configure hibernate, we need a Hibernate
Configuration class, inside it, we need to create asessionFactorywith thedataSource. -
Create entity class using
@Entityand@Table,@Id,@Column@GeneratedValueto map objects to the database. -
To use it, we call sessionFactory.getCurrentSession to perform operations.
-
To handle transactions, we can use @Transactional provided by Spring to handle transactions.
Migration between different databases
Change database URL, driver, username, password, dialect
Dialect is used to generate the SQL statement according to the typr of database.
Driver is used to set up the connection between the application and the database.
Entity State
-
transientstate, the entity instance is not attached to a session and has no corresponding rows in the database. It’s usually just a new object that has been created to save to the database. -
persistentstate, the entity instance is associated with a unique Session object (object already mapped to the database). Upon flushing the Session to the database, the entity is guaranteed to have a corresponding consistent record in the database. -
detachedstates, the entity instance was once attached to a Session, but now it’s not. An instance enters this state if it is evicted from the context, clear or close the Session, or put the instance through serialization/deserialization process.
Fetching Strategies
-
Eager: will fetch all attributes of an entity at once, including Aggregation / Composition. -
Lazy:Defaultwill load the Aggregation / Composition fields only when requested. This can improve performance by reducing the amount of data retrieved from the database
LazyInitializationException occurs when accessing a lazily-loaded proxy outside the session. Hibernate is unable to fetch the data because the session has been closed. We can use eager fetching to prevent this from happening, or manually initialize the collection before the session closes.
Hibernate Caching
There are two level Caching in Hibernate:
-
First levelcache provides caching at the session level. It is enabled by default. When you load an entity using a Session, Hibernate checks the first-level cache first to see if the entity is already loaded. If it’s found in the cache, Hibernate returns the cached object, avoiding a database query. We can use session contains() to check if an obj is cached or not. get(). load() methods. -
Second Levelcache is disabled by default, it is a higher level, cross-multi session. When query something, Hibernate will execute a query like select all fields from table where …, and cache all objects in second level cache, when hibernate need to query object by id, it will first check the first level cache, if not contains, then check the second level cache, if not contains too, it will fetch from database and put it into the second level cache. Second level cache is only used for querying by ID of Hibernate objects.
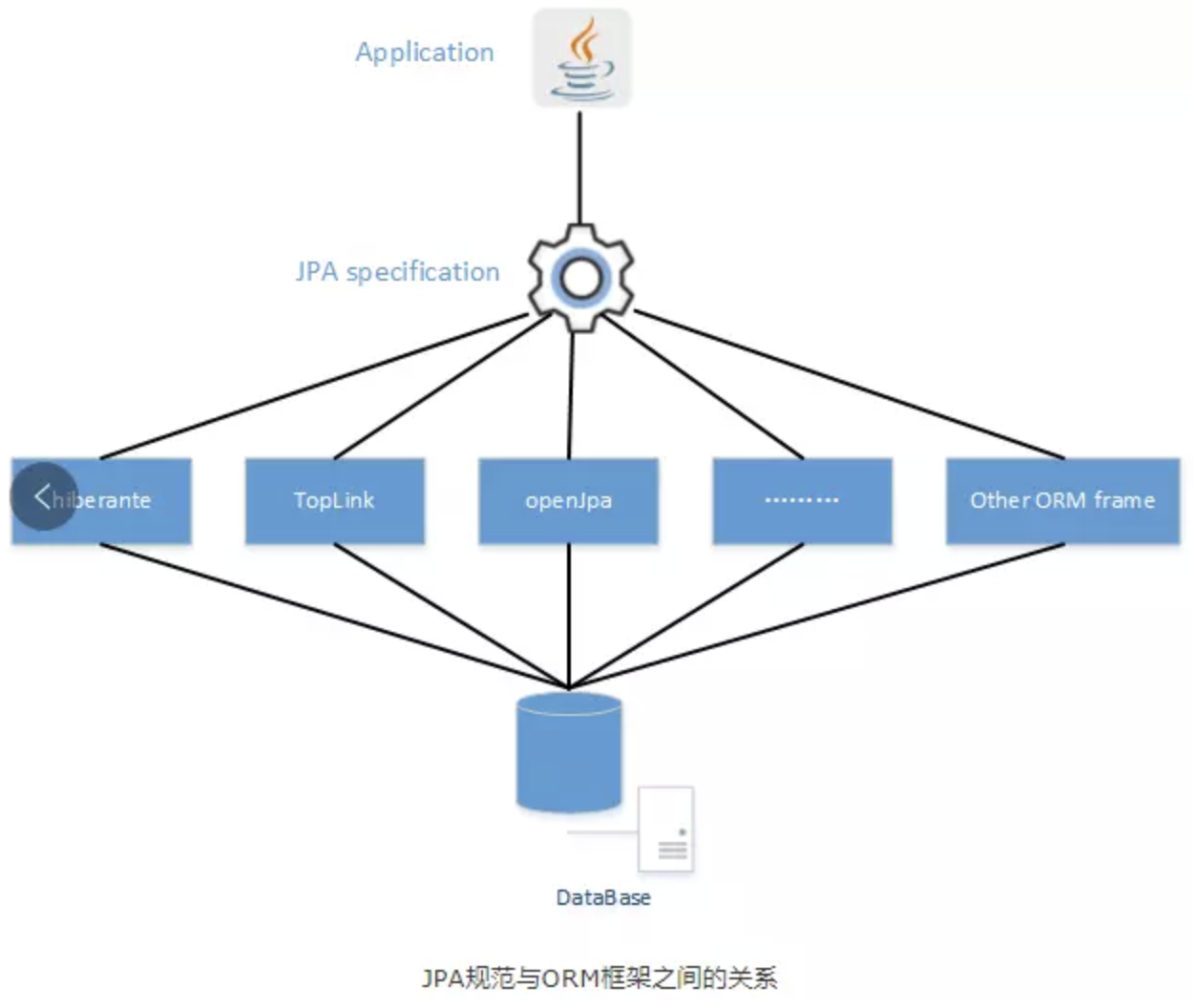
JPA (Java Persistence API)
JPA is a specification of Java. It is used to persist data between Java object and relational database. It doesn’t provide any implementation, so it need a provider to implement it like Hibernate, EclipseLink, TopLink, etc.
-
ORM mapping between Java object and relational database
@Entityannotation is used to map Java object to relational database@Tableannotation is used to map Java object to relational database table@Columnannotation is used to map Java object to relational database column@Idannotation is used to map Java object to relational database primary key@Transientannotation is used to ignore the field when mapping Java object to relational database
-
JPQL (Java Persistence Query Language)
- JPQL is a query language which is used to query data from relational database
- JPQL is similar to SQL, but it is object-oriented
- JPQL is database independent
-
EntityManager
- EntityManager is used to manage the lifecycle of entity, and perform CRUD operations.
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA is a framework which is built on top of JPA. It is used to simplify the development of JPA application.
Spring Data Repository
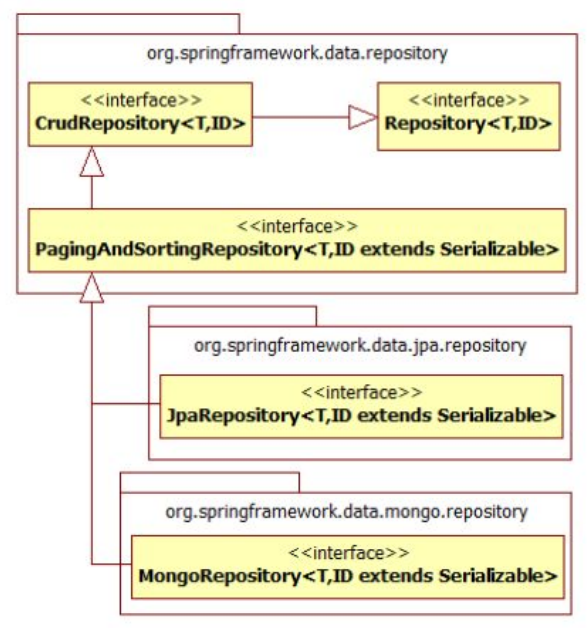
Spring Data Repository has different interfaces, and each interface is used to perform different operations.
-
Repositoryis the central interface in Spring Data repository abstraction. It is amarker interfaceto capture the types to work with and to help you to discover interfaces that extend this one. It is not used directly. -
CrudRepositoryprovides CRUD operations, it extendsRepositoryinterface.public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> { // Note that the ID here is a serializable which represent the id of the Entity <S extends T> S save(S entity); Optional<T> findById(ID primaryKey); Iterable<T> findAll(); long count(); void delete(T entity); boolean existsById(ID primaryKey); // … more functionality omitted. } -
PagingAndSortingRepositoryprovidespaginationandsortingoperations, it extendsCrudRepositoryinterface.public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> { Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort); Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable); } -
Query Feature
Using Spring Data Repository, we can define the query method by using the naming convention. In this way, we don’t need to write the query statement and the implementation of the query method.
The machanism strips the prefixes
find…By,read…By,query…By,count…By, andget…Byfrom the method and starts parsing the rest of it.interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> { List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname); // Enables the distinct flag for the query List<Person> findDistinctPeopleByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname); List<Person> findPeopleDistinctByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname); // Enabling ignoring case for an individual property List<Person> findByLastnameIgnoreCase(String lastname); // Enabling ignoring case for all suitable properties List<Person> findByLastnameAndFirstnameAllIgnoreCase(String lastname, String firstname); // Enabling static ORDER BY for a query List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameAsc(String lastname); List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameDesc(String lastname); }We can also use
@Queryannotation to define the query method.interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> { @Query("select u from User u where u.emailAddress = ?1") User findByEmailAddress(String emailAddress); }
NoSQL & MongoDB
SQL databases based on relational data models. well-defined structure with clear relationships and constraints
NoSQL (not only sql) databases use various data models, such as key-value, document, columnar, or graph. They provide flexible schemas that allow for dynamic and unstructured data. Like mongoDB, redis, Bigtable
Use Relational database:
- needs strong transactional support
- data has a well-defined structure with clear relationships
- requires complex queries involving multiple tables, joins, and aggregations
Use Non-Relational DB:
- Data is unstructured, like LinkedIn, user profile, each user may have different sections, if you put it in RDB, there will be many empty fields, so using Nosql will decrease the space and increase the speed for reading.
- Need high-speed read and write operations
- Distributed and Cloud Environments: NoSQL databases are well-suited for distributed and cloud-based architectures, allowing you to distribute data across multiple nodes or data centers.
Mockito
Mockito is a mocking framework used for unit testing of Java applications. When we write unit tests, we need to mock the external dependencies. Mockito provide an easy way to mock the dependencies.
Difference between @Mock, @Spy, @InjectMocks
@Mock is used to create and inject mocked instances. Often used to mock the dao layer. It will not call the real method inside.
@InjectMocks will inject the mocked instances into the tested object automatically. Often used to mock the service layer. It will call the real method inside. (suppose we are testing service layer, the service should be marked as @InjectMocks. becasue we need to run the logic inside each method)
@Spy is used to create and inject partially mocked instances. It will call the real method inside. It is used when we want to call the real method and perform some logic inside the method. like sending an email and then test if the email is sent successfully.
What is the difference between @Mock and @MockBean? (same with @Spy and @SpyBean)
They both are used to create a fake object. @Mock create object not related to the spring framework.
When testing controller, it need us to start the Spring Boot application. We use @MockBean to create a fake object that is part of the Spring context. such as beans declared in the application’s configuration or beans created by Spring Boot auto-configuration.
ArgumentCaptor receive the parameter of the mocked method
We can use ArgumentCaptor to capture the parameter of the mocked method.
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<User> userCaptor;
@Test
public void testCreateUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("Chris");
user.setEmail("xx@gmail.com");
userService.createUser(user);
verify(userDao).save(userCaptor.capture());
assertEquals("Chris", userCaptor.getValue().getName());
}
